RBI's Monetary Action
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently reduced the repo rate by 25 basis points to 5.25%. This move has set the stage for a series of adjustments in the banking
sector. The repo rate cut serves as a signal to the banks, which typically respond by reevaluating their own interest rates on loans and deposits. This chain reaction directly impacts both borrowers, who may see a reduction in their loan EMIs, and depositors, who might experience changes in their returns on fixed deposits.
Banks React Swiftly
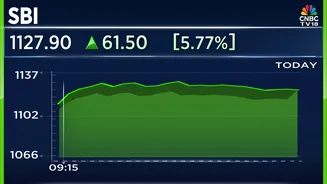
In response to the RBI's repo rate cut, multiple banks have promptly lowered their lending rates. Institutions such as HDFC Bank, PNB, and Canara Bank have announced reductions. The adjustments aim to pass on the benefits of the lower borrowing cost to customers. These rate cuts are designed to make borrowing more affordable. The effect includes lower home loan interest rates, potentially leading to reduced monthly installments, and revised interest rates on fixed deposits, influencing the returns available to savers.
Loan Rate Reductions
Home loans, in particular, have seen considerable adjustments. For instance, PNB lowered its home loan rate to 8.10% following the RBI's rate cut. Such changes are vital for prospective homeowners, as they directly impact the affordability of purchasing property. The cut in interest rates can translate to substantial savings over the lifespan of a home loan. The banks' actions are geared towards maintaining competitive positioning within the market and attracting new customers.
Impact on Deposits
The adjustments aren't only limited to lending products. Banks also modify interest rates on fixed deposits. This means that depositors will experience a shift in the returns they receive on their savings. These changes have to be understood by individuals planning their investments, as they directly influence the return on their capital. Although interest rates on deposits may change, there is still the potential to get competitive returns.
Broader Economic Effects
The RBI's and the banks' movements have broader repercussions for the economy. Reduced borrowing costs can stimulate economic activity by encouraging investments and consumer spending. These actions also play a part in managing inflation by making credit more accessible. Moreover, these changes can affect the overall financial health of businesses and individuals, setting the tone for the market.