What's Happening?
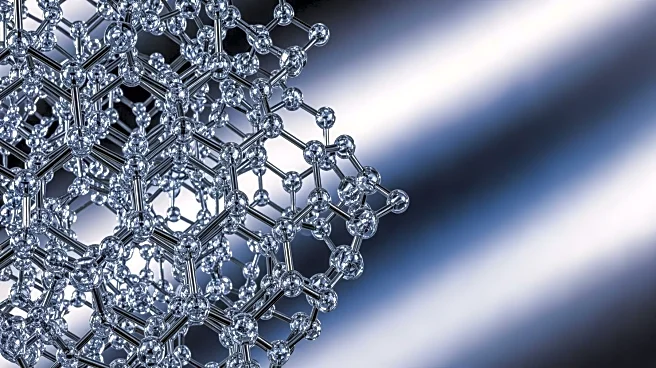
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2025 was awarded to Susumu Kitagawa, Richard Robson, and Omar Yaghi for their pioneering work in the development of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). These frameworks are porous
structures composed of organic linker molecules connected by metal nodes, which have been synthesized in thousands of variations over the past 30 years. MOFs have practical applications in storing and capturing gases to reduce pollution, trapping harmful substances, and harvesting water from arid environments. The commercialization of MOFs is evident in companies across different continents. The award highlights the significant contributions of Kitagawa, Robson, and Yaghi in advancing the field, with Robson's early work on crystalline structures and Yaghi's introduction of the term 'metal-organic framework' in 1995. Kitagawa's research focused on the dynamic design of MOFs, leading to innovations in gas adsorption and structural transformations.
Why It's Important?
The recognition of MOFs through the Nobel Prize underscores their transformative impact on environmental and industrial applications. MOFs offer solutions for pollution control and resource management, such as water harvesting in desert regions. Their ability to store and separate gases has implications for energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. The award not only celebrates scientific innovation but also encourages further research and development in the field, potentially leading to new technologies and commercial opportunities. The global interest in MOFs, as demonstrated by the EuroMOF conference, indicates a growing network of researchers and industries invested in these materials, which could drive advancements in environmental technology and materials science.
What's Next?
Following the Nobel Prize recognition, increased attention and funding for MOF research are expected, potentially accelerating the development of new applications and commercial products. Researchers may explore further innovations in MOF design and functionality, expanding their use in various industries. The award could also inspire collaborations between academia and industry, fostering the translation of scientific discoveries into practical solutions. As MOFs continue to gain prominence, stakeholders in environmental technology and materials science may prioritize investments in this area, anticipating breakthroughs that address global challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity.
Beyond the Headlines
The development of MOFs represents a significant shift in materials science, emphasizing the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation. The ability to design frameworks with specific properties opens up possibilities for tailored solutions in environmental and industrial contexts. Ethical considerations may arise regarding the deployment of MOFs, particularly in regions facing resource scarcity or environmental degradation. The long-term impact of MOFs on sustainability and resource management could redefine approaches to pollution control and energy efficiency, highlighting the need for responsible and equitable implementation of these technologies.