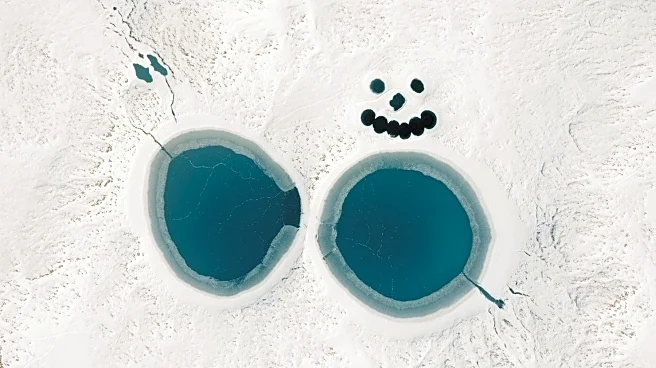
What's Happening?
NASA's Landsat 8 has captured an image of a series of oval lagoons in Siberia that form the shape of a snowman when viewed from above. Located near the village of Billings on Russia's Chukchi Peninsula, these natural formations are the result of geological
processes involving ice wedges and thermokarst lakes. Despite the warmest month being June, the area remains covered in ice due to its Arctic location. The image highlights the unique natural beauty and geological history of the region.
Why It's Important?
This image provides insight into the geological processes that shape Arctic landscapes, offering valuable data for scientists studying climate change and its impact on polar regions. Understanding these natural formations can help researchers track environmental changes over time, contributing to broader climate studies. The image also serves as a reminder of the diverse and often surprising natural phenomena that occur in remote parts of the world.
Beyond the Headlines
The snowman-shaped lagoons are not only a geological curiosity but also a cultural touchstone, connecting modern observations with historical exploration. The region's history of exploration, including the use of reindeer for transportation by indigenous peoples and early explorers, adds a layer of human interest to the scientific data. This intersection of natural and cultural history enriches our understanding of the Arctic and its significance.