What's Happening?
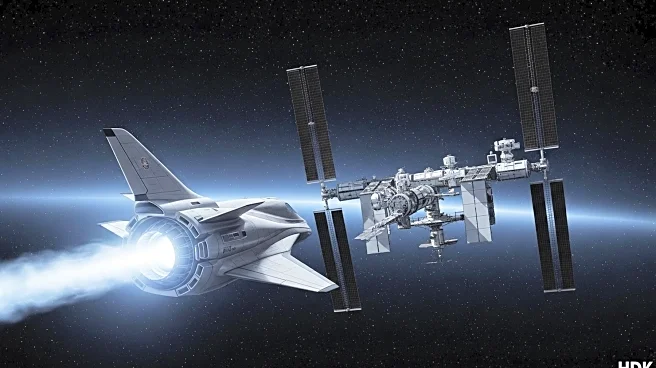
Northrop Grumman's latest supply mission to the International Space Station (ISS) has encountered a significant setback due to engine trouble. The Cygnus capsule, which was launched aboard a SpaceX rocket from Florida, experienced a premature shutdown of its main engine while attempting to boost its orbit. This issue has delayed the capsule's scheduled docking with the ISS, which was planned for Wednesday. The Cygnus XL, Northrop Grumman's newest and largest model, was carrying over 11,000 pounds of cargo, including food, science experiments, and spare parts for the station's systems. NASA and Northrop Grumman are currently assessing alternative plans to resolve the situation. This mission marks a critical test for the Cygnus XL's increased capacity, which is designed to enhance the efficiency of supply deliveries to the ISS.
Why It's Important?
The delay in the supply delivery to the ISS underscores the challenges and risks associated with space missions, particularly those involving new technology. Northrop Grumman is one of NASA's primary cargo suppliers, alongside SpaceX, and any disruption in their operations can impact the ISS's functioning and the well-being of its crew. The cargo includes essential supplies and scientific equipment, which are vital for ongoing research and daily operations aboard the station. The incident highlights the importance of reliable technology in space exploration and the need for contingency plans to address unexpected technical failures. The outcome of this situation could influence future collaborations and contracts between NASA and its commercial partners.
What's Next?
NASA and Northrop Grumman are working to devise an alternative plan to ensure the Cygnus capsule can safely reach the ISS. This may involve troubleshooting the engine issue or potentially rescheduling the docking attempt. The resolution of this problem will be closely monitored by stakeholders in the aerospace industry, as it could affect future missions and the development of similar technologies. Additionally, the incident may prompt a review of the Cygnus XL's design and operational protocols to prevent similar occurrences in future missions.