What's Happening?
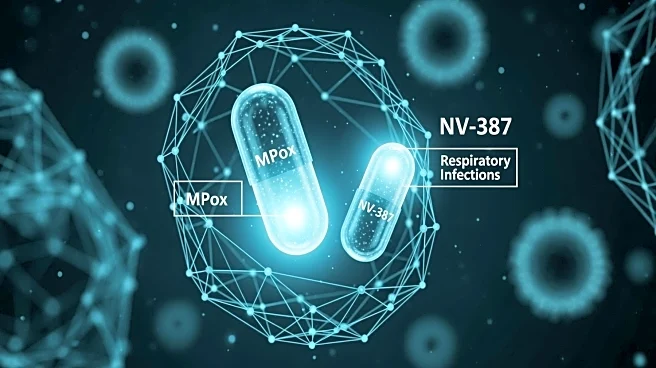
NanoViricides, Inc. has announced a dual-track clinical development strategy for its antiviral drug candidate NV-387. The company aims to address unmet medical needs for effective broad-spectrum antiviral therapies.
NV-387, which utilizes nano-polymer micelle technology, is designed to bind and destroy virus particles in the blood, preventing them from infecting cells. The first clinical trial will target the MPox virus, a relative of smallpox, with potential biodefense applications. Ethics approval for a Phase 2 trial in Congo has been obtained, and a successful trial could lead to development funding from the US biodefense agency BARDA. The second trial will focus on respiratory viral diseases, including influenza, RSV, and coronaviruses, with an adaptive basket-type trial planned in India. This strategy could lead to focused US trials starting in 2027.
Why It's Important?
The development of NV-387 is significant as it addresses the need for broad-spectrum antiviral therapies, particularly in the context of emerging viral threats like MPox and respiratory infections. The potential funding from BARDA highlights the importance of biodefense applications, which could enhance national security against biological threats. The trials in Congo and India could provide critical data on the efficacy of NV-387, potentially leading to its approval and commercialization in the US market. Success in these trials could open up substantial market opportunities, with independent estimates suggesting a $2.6 billion opportunity in RSV and $4.6 billion in influenza.
What's Next?
NanoViricides plans to advance NV-387 into Phase II human clinical trials, with the MPox trial potentially starting by late 2025 or early 2026. The respiratory viral diseases trial in India might begin in winter 2026, with US trials possibly following in 2027. The company is focused on obtaining necessary regulatory approvals and securing funding for further development. The success of these trials could lead to broader commercialization and licensing opportunities, expanding the company's reach in the antiviral market.
Beyond the Headlines
The development of NV-387 could have long-term implications for antiviral therapy, potentially setting a precedent for the use of nanotechnology in medicine. The ethical considerations of conducting trials in different countries, particularly in regions with endemic diseases, highlight the need for careful oversight and collaboration with local health authorities. The success of NV-387 could also influence future research and development strategies in the pharmaceutical industry, encouraging more investment in nanotechnology-based solutions.