What's Happening?
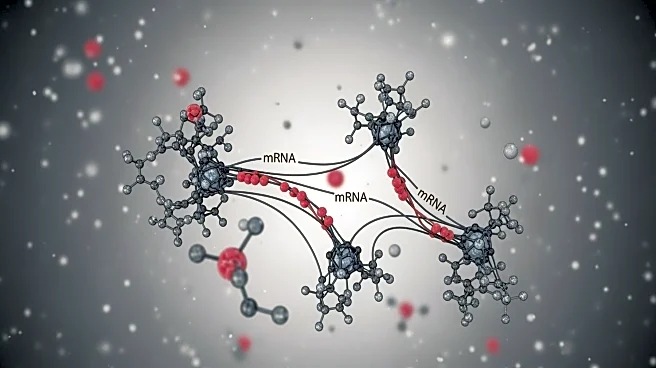
Research has revealed that the interaction between G3BP1 and Caprin1 proteins plays a crucial role in mRNA recruitment during cellular stress responses. G3BP1, a cytoplasmic RNA-binding protein, forms
condensates with Caprin1, facilitating the assembly of stress granules (SGs) under oxidative stress conditions. The study utilized a microtubule bench assay to demonstrate that Caprin1 enhances mRNA recruitment to G3BP1, highlighting the importance of protein-protein interactions in cellular stress mechanisms. The findings suggest that Caprin1's presence significantly influences the mRNA composition of stress granules, potentially affecting cellular resilience to stress.
Why It's Important?
Understanding the molecular interactions that govern stress granule assembly is vital for developing therapeutic strategies against diseases linked to cellular stress, such as neurodegenerative disorders. The G3BP1-Caprin1 interaction offers insights into the regulation of mRNA dynamics, which could inform the design of interventions to modulate stress responses. This research underscores the complexity of cellular stress mechanisms and the potential for targeting specific protein interactions to enhance cellular resilience and prevent disease progression.
What's Next?
Further studies are needed to explore the therapeutic potential of modulating G3BP1 and Caprin1 interactions in disease contexts. Investigating the role of other RNA-binding proteins in stress granule dynamics could provide a more comprehensive understanding of cellular stress responses. Additionally, the development of small molecules or peptides that can influence these interactions may offer new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Beyond the Headlines
The study raises questions about the broader implications of protein interactions in cellular stress responses and their potential impact on health and disease. As research progresses, ethical considerations regarding the manipulation of cellular processes for therapeutic purposes will need to be addressed. The balance between scientific advancement and ethical responsibility will be crucial in the application of these findings.