What's Happening?
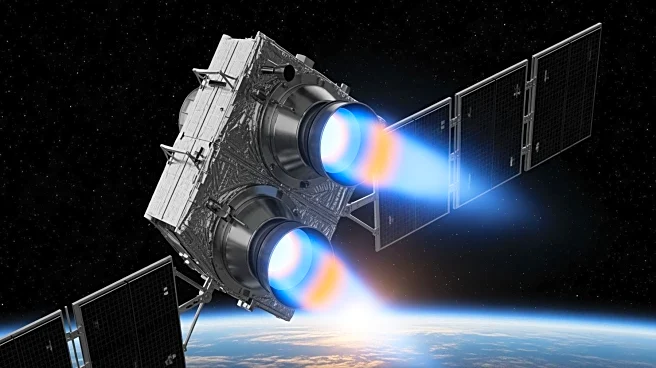
NASA has initiated an in-space test of two innovative micropropulsion technologies aboard a CubeSat named DUPLEX (Dual Propulsion Experiment). Deployed from the International Space Station on December
2, 2025, DUPLEX is equipped with two thruster systems designed to improve the maneuverability and operational efficiency of small spacecraft. The first system, a fiber-fed pulsed plasma thruster, uses electric pulses to vaporize Teflon, generating ions for efficient thrust with minimal fuel consumption. The second system, inspired by 3D printing technology, vaporizes a polymer called Delrin to produce continuous thrust. These technologies aim to provide safer, more affordable propulsion solutions compared to existing systems. Over the next two years, DUPLEX will demonstrate its capabilities by adjusting its orbit, showcasing the potential for these systems to maintain and maneuver spacecraft in low Earth orbit and beyond.
Why It's Important?
The successful deployment and testing of these propulsion technologies could significantly impact the U.S. space industry by offering cost-effective and efficient solutions for spacecraft maneuverability. This advancement is crucial for maintaining and adjusting orbits, avoiding space debris, and coordinating spacecraft operations, which are essential for the growing low Earth orbit economy. Furthermore, these technologies could enable extended missions to the Moon, Mars, and other distant locations, supporting NASA's long-term exploration goals. By enhancing the capabilities of small spacecraft, NASA and its commercial partners can strengthen the U.S. position in the global space market, fostering innovation and economic growth.
What's Next?
As DUPLEX continues its mission, NASA and its partners will monitor the performance of the propulsion systems to validate their effectiveness in real-world conditions. Successful tests could lead to broader adoption of these technologies in future spacecraft designs, potentially transforming how small satellites operate in space. This could also encourage further collaboration between NASA and commercial entities, driving advancements in space technology and expanding the possibilities for space exploration and commercial activities.