What's Happening?
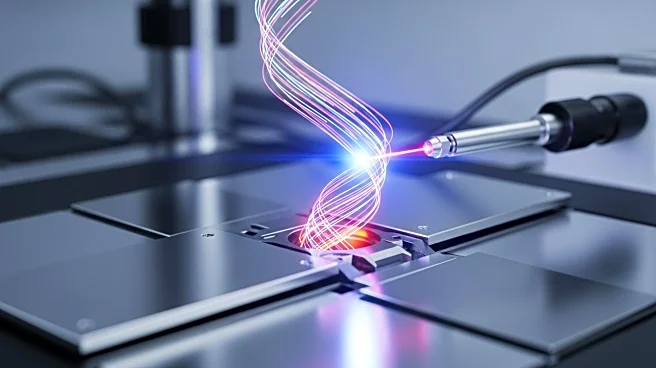
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter have developed a method to control a material behavior known as ferroaxiality using circularly polarized lasers. This behavior, similar to magnetism, has been elusive and could lead to the development of more efficient and stable memory devices. The team used a compound of rubidium, iron, molybdenum, and oxygen, and applied circularly polarized laser light to impart rotation onto the material's atoms, effectively switching the direction of motion of the dipoles. This breakthrough adds to the array of options for building hard drives where information is stored in patterns of electromagnetic charge. However, the experiment requires cooling the material to -70°C and uses a large laser system, indicating that practical applications are still in the developmental stage.
Why It's Important?
The ability to control ferroaxiality with lasers opens new possibilities for the development of advanced memory devices, potentially revolutionizing data storage technology. This could lead to more efficient hard drives, enhancing the performance and stability of electronic devices. The research highlights the potential for laser technology to manipulate material properties, which could have significant implications for the electronics industry. As the demand for faster and more reliable data storage solutions grows, this innovation could provide a competitive edge in the market, benefiting manufacturers and consumers alike.
What's Next?
Further research is needed to refine the laser control technique and address the practical challenges of cooling and system size. The team aims to develop smaller and more efficient laser systems that can operate at room temperature, making the technology viable for commercial applications. Collaboration with industry partners could accelerate the development process and lead to the integration of this technology into consumer products. As the research progresses, stakeholders in the electronics and data storage sectors will be closely monitoring developments, potentially leading to new partnerships and investments.
Beyond the Headlines
The ethical implications of advanced memory devices include concerns about data privacy and security. As storage technology becomes more sophisticated, ensuring the protection of sensitive information will be crucial. Additionally, the environmental impact of manufacturing new devices must be considered, as the demand for rare materials and energy-intensive processes could contribute to resource depletion and pollution. Balancing technological advancement with sustainability and ethical considerations will be key to the responsible development of this technology.