What's Happening?
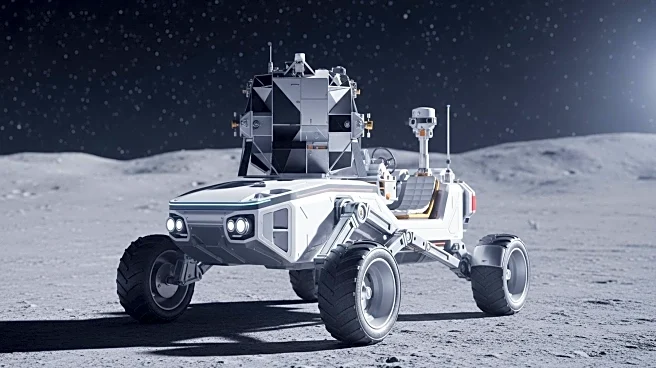
Blue Origin has been awarded a significant NASA contract to transport the VIPER rover to the lunar south pole using its Blue Moon Mk1 lander. This contract, valued at approximately $190 million, is part of NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services task order. The VIPER rover, which stands for Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, aims to explore potential water ice deposits on the Moon. This development follows NASA's previous cancellation of the VIPER program due to delays and cost overruns. The rover will be equipped with instruments to detect water, hydrogen, and other minerals, contributing to NASA's long-term lunar exploration goals.
Why It's Important?
The contract represents a crucial endorsement of Blue Origin's capabilities in lunar exploration, marking its first high-profile scientific payload. The successful deployment of the VIPER rover could significantly advance NASA's understanding of lunar resources, which are vital for sustaining future human presence on the Moon. Extracting resources in-situ, such as water ice, could be transformed into essential supplies like drinking water, oxygen, and rocket fuel, reducing the need to transport these from Earth. This mission aligns with broader goals of establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon.
What's Next?
The VIPER rover is scheduled to be delivered to the lunar surface by late 2027. It will spend approximately 100 days on the Moon, conducting scientific investigations and mapping water ice deposits. The success of this mission could pave the way for further lunar exploration initiatives and collaborations between NASA and private companies like Blue Origin. The findings from VIPER's mission will be crucial for planning future lunar missions and potentially establishing a permanent human settlement on the Moon.