What's Happening?
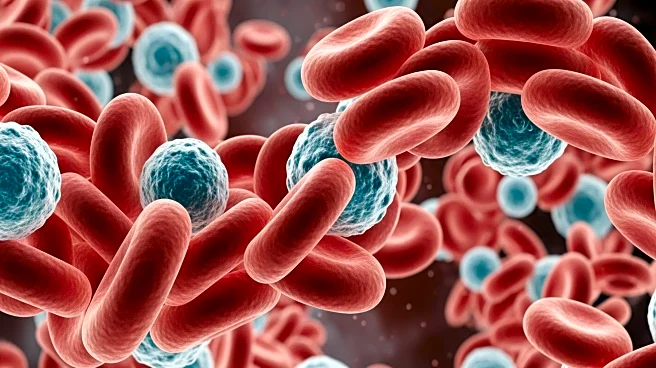
A recent exploration into the complexity of blood has revealed its multifaceted role in human biology, emphasizing its critical functions beyond mere oxygen transportation. Blood, a vital component of the human body, is composed of red and white blood cells,
plasma, and platelets, each playing a unique role in maintaining health. Red blood cells, for instance, are responsible for oxygen delivery, facilitated by the protein haemoglobin, which shares structural similarities with chlorophyll. This discovery underscores the intricate design of blood, which scientists continue to study with awe. Recent findings have also highlighted a new mechanism where red blood cells contribute to blood clotting under low oxygen conditions, challenging previous assumptions about platelet dominance in this process. Additionally, advancements in regenerative medicine have shown potential in using blood peptides for 3D-printed bone repair scaffolds, further demonstrating blood's regenerative capabilities.
Why It's Important?
The study of blood's complexity has significant implications for medical science and healthcare. Understanding the precise mechanisms of blood functions can lead to breakthroughs in treating various conditions, such as heart attacks and internal injuries, by leveraging the body's natural processes. The discovery of red blood cells' role in clotting could revolutionize how medical professionals approach vascular injuries and clotting disorders. Furthermore, the potential use of blood-derived materials in regenerative medicine could pave the way for innovative treatments in bone repair and other areas. These insights not only enhance our understanding of human biology but also open new avenues for medical research and therapeutic applications, potentially improving patient outcomes and healthcare practices.
What's Next?
Future research is likely to focus on further unraveling the complexities of blood and its components. Scientists may explore the potential of artificial blood substitutes, although current findings suggest that replicating the full functionality of natural blood remains a challenge. Continued studies on blood's role in various physiological processes could lead to new medical technologies and treatments. Additionally, the ethical and practical implications of using blood-derived materials in medicine will need to be addressed as these technologies advance. Stakeholders in the medical and scientific communities will likely engage in discussions about the integration of these findings into clinical practice, aiming to enhance patient care and treatment efficacy.
Beyond the Headlines
The exploration of blood's complexity raises philosophical and ethical questions about the nature of life and the possibility of intelligent design. The precise and multifaceted functions of blood suggest a level of complexity that some argue points to intentional creation rather than random chance. This perspective challenges traditional scientific views and invites further debate on the origins and intricacies of biological systems. As research continues, these discussions may influence how society perceives the relationship between science and philosophy, potentially impacting educational and cultural narratives.