What's Happening?
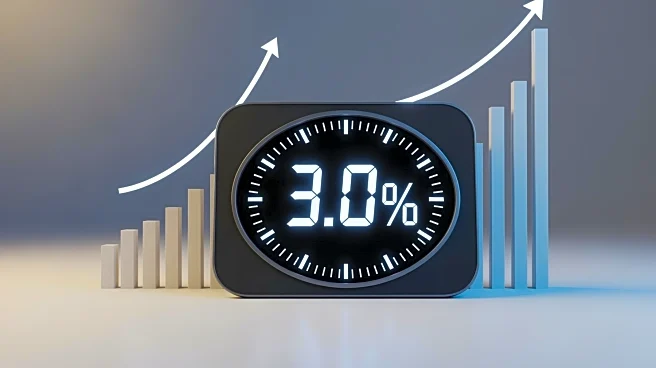
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported a 0.3 percent increase in the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) in September 2025, following a 0.4 percent rise in August. Over the past
12 months, the all items index increased by 3.0 percent. The rise in gasoline prices, which went up by 4.1 percent, was a significant contributor to the monthly increase. Other notable increases were seen in the food index, which rose by 0.2 percent, and the energy index, which increased by 1.5 percent.
Why It's Important?
The CPI is a critical measure of inflation, reflecting changes in the cost of living for urban consumers. A 3.0 percent increase indicates inflationary pressures that could affect consumer purchasing power and economic stability. Rising energy and food prices can lead to higher living costs, impacting household budgets and potentially slowing consumer spending. Policymakers and economists closely watch these trends to adjust economic policies accordingly.
What's Next?
The Federal Reserve may consider policy adjustments to address the inflation rate, which remains above its target. Potential measures include interest rate hikes to control inflationary pressures. Consumers and businesses will need to adapt to changing economic conditions, possibly adjusting spending and investment strategies.
Beyond the Headlines
Inflation can have broader economic implications, such as influencing wage negotiations and impacting social equity. Policymakers must balance inflation control with economic growth and employment objectives, ensuring that measures do not disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.