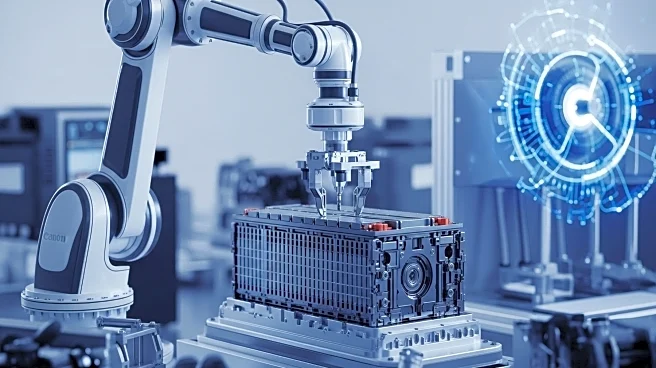
What's Happening?
Recirculate, a project funded by the European Union, is advancing innovations in the battery industry by developing a state-of-the-art electric vehicle (EV) battery disassembly system using artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. The project aims to address significant bottlenecks in the battery industry, such as safe and efficient disassembly, by automating the process from battery pack to cell level. The system utilizes machine learning models to identify and extract critical components, including screws and connectors, and employs a robotic cell equipped with a Kuka KR10 industrial robot. This robot autonomously detects, unscrews, and removes components of high-voltage battery packs, enhancing precision and efficiency in the disassembly process. The innovation is led by Centria University of Applied Sciences, which has developed tools capable of detecting and manipulating parts with remarkable precision, marking a significant step towards industrial application.
Why It's Important?
The development of an AI-driven battery disassembly system is crucial for advancing the circular economy in the battery industry. By automating the disassembly process, Recirculate's innovation reduces the need for manual labor, increases efficiency, and enhances safety in handling high-voltage battery packs. This technology not only supports sustainable practices by facilitating the recycling and reuse of battery components but also addresses environmental concerns associated with battery waste. The ability to accurately identify and disassemble batteries from major manufacturers like Ford and Tesla further underscores the system's potential to streamline operations across the industry. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, such advancements are essential for meeting sustainability goals and reducing the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
What's Next?
The team at Centria University of Applied Sciences is focused on scaling the solution and extending compatibility to other battery types by expanding its proprietary training dataset. This effort aims to enhance the system's adaptability and efficiency in disassembling various battery models, thereby broadening its application across the industry. As the project progresses, stakeholders in the battery and automotive sectors may explore partnerships or investments to integrate this technology into their operations, potentially leading to widespread adoption. Additionally, regulatory bodies may consider updating policies to support the use of AI and robotics in battery recycling, further promoting sustainable practices.
Beyond the Headlines
The integration of AI and robotics in battery disassembly not only represents a technological advancement but also raises ethical and legal considerations regarding automation and labor displacement. As industries increasingly adopt automated systems, there may be discussions around the impact on employment and the need for workforce retraining. Furthermore, the project's success could influence global standards for battery recycling, encouraging other regions to adopt similar technologies and practices. The long-term implications of such innovations may include shifts in manufacturing processes and supply chain dynamics, as well as increased collaboration between technology developers and environmental organizations.