What's Happening?
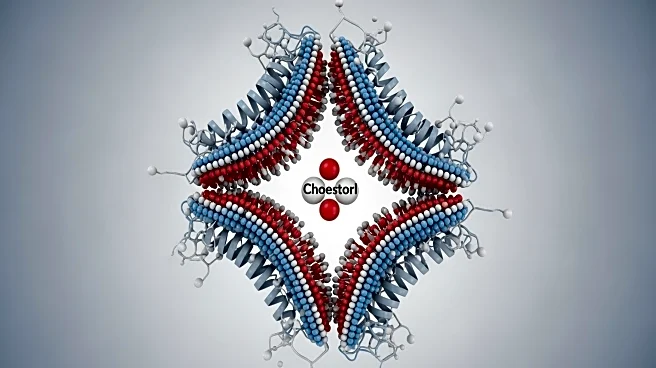
Research has revealed the mechanisms of cholesterol attraction in transmembrane helices, highlighting the role of cholesterol recognition amino acid consensus motifs (CRAC motifs) and their inverse (CARC motif). The study used bioinformatics, molecular
modeling, and simulations to show that cholesterol recognition is influenced by thermodynamic forces and structural features of transmembrane helices, such as hydrophobic length and accessible surface area.
Why It's Important?
Understanding cholesterol attraction mechanisms could have implications for drug development and membrane protein research. The findings highlight the importance of amino acid composition and structural features in cholesterol binding, potentially guiding the design of therapeutic interventions targeting membrane proteins. The study also emphasizes the role of cholesterol in cellular processes and its impact on health.
What's Next?
Future research may focus on exploring the therapeutic potential of modulating cholesterol attraction in transmembrane proteins. This could involve developing drugs that target specific motifs or structural features. The findings may also influence studies on the role of cholesterol in disease development and prevention.
Beyond the Headlines
The research raises ethical considerations about manipulating cholesterol pathways and the potential impact on health. It highlights the importance of understanding the balance between cholesterol attraction and cellular function in drug development. The findings could drive discussions on the role of cholesterol in health and disease.