What's Happening?
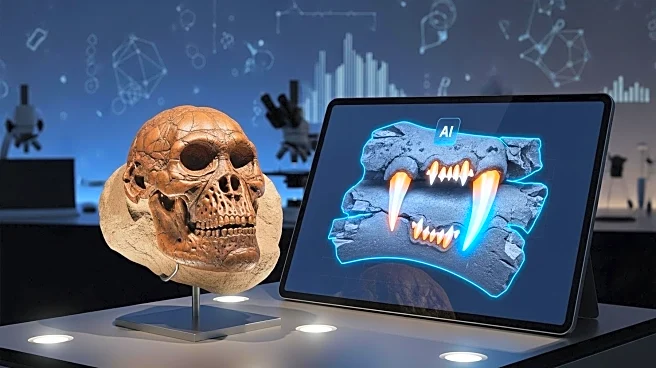
Recent analysis using AI technology has revealed that Homo habilis fossils found at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania were likely consumed by leopards. The fossils, known as OH7 and OH65, date back approximately 1.8 to 1.85 million years. Previous studies suggested these individuals were hunted by large carnivores, but the specific predator was unidentified. Researchers from the University of Alcalá and Rice University trained AI models to recognize tooth marks from various carnivores, achieving over 90% accuracy. The AI identified leopard bite marks on the fossils, supporting the theory that leopards were responsible for the consumption of these early human ancestors.
Why It's Important?
This discovery provides significant insights into the predatory threats faced by early human ancestors and the ecological dynamics of their environment. Understanding the interactions between Homo habilis and predators like leopards can shed light on the evolutionary pressures that shaped human development. The use of AI in paleontology represents a technological advancement, offering more precise methods for analyzing fossil evidence and reconstructing historical ecosystems. This could lead to more accurate interpretations of fossil records and enhance our understanding of human evolution.
What's Next?
The application of AI in fossil analysis may expand to other archaeological sites, potentially uncovering new information about the interactions between early humans and their environment. Researchers might continue to refine AI models to improve accuracy and apply them to other fossilized remains, broadening the scope of paleontological studies. This could lead to collaborations between technology experts and archaeologists, fostering interdisciplinary research that enhances the study of human history.
Beyond the Headlines
The integration of AI in archaeological research raises ethical considerations regarding the interpretation of historical data. As AI becomes more prevalent in scientific studies, ensuring transparency and accuracy in its application is crucial. Additionally, this technological approach may influence the methods used in other fields, such as anthropology and ecology, promoting a shift towards more data-driven research.