What's Happening?
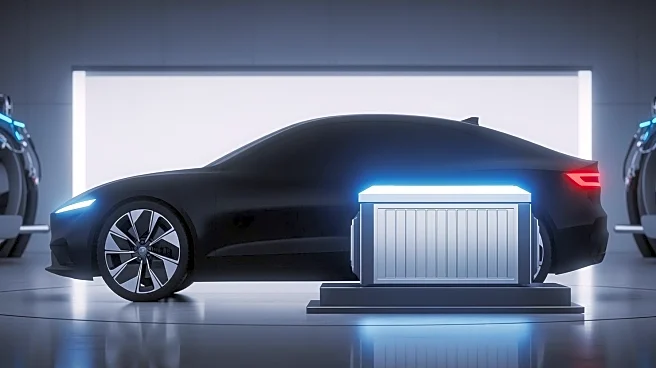
Toyota, one of the world's largest car manufacturers, has announced plans to mass-produce solid-state batteries for electric vehicles (EVs), aiming to launch a new line of cars featuring this technology
by 2027 or 2028. In collaboration with Sumitomo Metal Mining Company, Toyota is developing cathode materials for these batteries, which promise longer life and faster charging compared to current lithium-ion technologies. Solid-state batteries replace the liquid electrolyte found in lithium-ion batteries with a solid, reducing fire risk and potentially increasing energy density. This development is part of a broader industry trend, with other automakers like Honda, Nissan, BMW, and Volkswagen also pursuing solid-state battery technology.
Why It's Important?
The introduction of solid-state batteries represents a significant advancement in EV technology, potentially transforming the automotive industry by offering safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting power sources. This could accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to environmental sustainability. For Toyota, this move positions the company as a leader in innovative battery technology, potentially increasing its market share in the growing EV sector. The collaboration with Sumitomo Metal Mining highlights the importance of strategic partnerships in advancing technological breakthroughs.
What's Next?
Toyota and Sumitomo Metal Mining plan to begin supplying the newly developed cathode materials by 2028, prioritizing Toyota's needs before expanding to meet broader market demand. As the industry moves towards solid-state batteries, other automakers are expected to intensify their research and development efforts to remain competitive. The successful implementation of this technology could lead to further innovations in battery design and performance, influencing future automotive trends and consumer preferences.
Beyond the Headlines
The shift to solid-state batteries may have broader implications beyond the automotive industry, potentially impacting sectors such as renewable energy storage and consumer electronics. The reduced fire risk and increased energy density could lead to safer and more efficient energy solutions across various applications. Additionally, the development of solid-state batteries may drive advancements in material science, leading to new discoveries and technologies.