What's Happening?
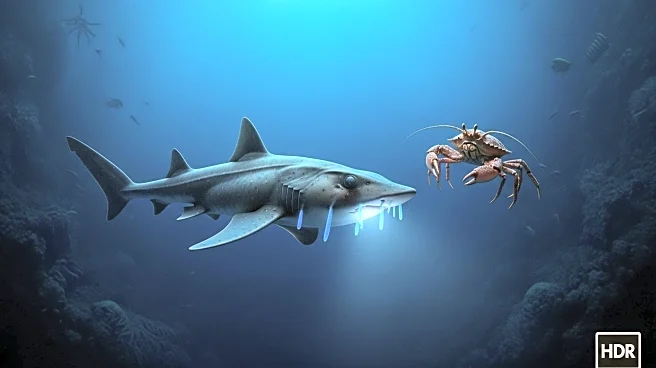
Researchers have identified two new species from deep-sea expeditions led by CSIRO, Australia's national science agency. The West Australian Lanternshark, Etmopterus westraliensis, was discovered at depths of up to 610 meters in the Gascoyne Marine Park area off Western Australia. This small shark, measuring up to 407 millimeters, is notable for its bioluminescence, with light produced by photophores on its belly and flanks. The species name honors the region of its discovery. Additionally, a new species of porcelain crab, Porcellanella brevidentata, was found along the Ningaloo coast at depths of up to 122 meters. This crab lives symbiotically with sea pens, soft corals related to sea fans, and is adapted to hide among the host's leaves. The crab is a filter feeder, using modified mouthparts to sweep water for plankton. These discoveries were part of a 2022 voyage on the CSIRO research vessel Investigator, which has led to the identification of nearly 20 new species.
Why It's Important?
The discovery of new marine species highlights the rich biodiversity of deep-sea environments, which remain largely unexplored. Understanding these ecosystems is crucial for conservation efforts and for advancing scientific knowledge about marine life. The identification of new species like the West Australian Lanternshark and Porcellanella brevidentata contributes to the broader understanding of marine biodiversity and ecological interactions. These findings can inform environmental policies and management strategies, particularly in marine protected areas. The ongoing research and upcoming expeditions promise further discoveries, potentially revealing hundreds of new species, which could have implications for marine biology and conservation.
What's Next?
Researchers plan to continue their exploration of deep-sea biodiversity with an upcoming CSIRO-led voyage to the Coral Sea Marine Park. This expedition aims to survey marine life and potentially discover more species new to science. The voyage will involve many of the same researchers from the 2022 expedition, along with new collaborators. These efforts are part of a broader initiative to enhance understanding of marine ecosystems and contribute to global biodiversity records. The findings from these expeditions may lead to new scientific insights and conservation strategies, emphasizing the importance of protecting marine habitats.
Beyond the Headlines
The discovery of new species in deep-sea environments underscores the importance of scientific exploration in uncovering the mysteries of the ocean. These findings highlight the potential for new ecological and evolutionary insights, as well as the need for sustainable management of marine resources. The bioluminescence of the West Australian Lanternshark, for example, could offer clues about adaptation mechanisms in deep-sea organisms. The symbiotic relationship between the porcelain crab and sea pens may provide insights into ecological interactions and the evolution of marine species. These discoveries contribute to the broader narrative of biodiversity and the interconnectedness of life on Earth.