What's Happening?
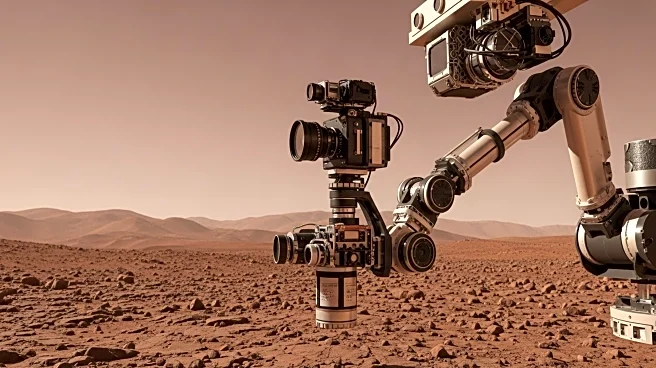
NASA's Mars rover Curiosity has captured detailed images using its Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on Sol 1375 of the Mars Science Laboratory Mission. The MAHLI, located on the turret at the end of the rover's robotic arm, was used to acquire images on June 19, 2016. The focus motor count position during the image acquisition was 13014, indicating the internal position of the MAHLI lens. This count helps determine whether the dust cover was open or closed, and can estimate the distance between the MAHLI lens and the target. The images are typically acquired using sunlight as an illumination source, although MAHLI's white light LEDs and ultraviolet LEDs can also be used. The images provide scales in micrometers per pixel, offering insights into the surface composition and features of Mars.
Why It's Important?
The use of MAHLI by NASA's Curiosity rover is crucial for understanding the Martian surface. These detailed images help scientists analyze the planet's geology, which is essential for future exploration missions. The ability to estimate distances and scales allows for precise scientific measurements, aiding in the study of Mars' history and potential habitability. This data contributes to the broader goals of space exploration, including the search for signs of past life and the assessment of resources for future human missions. The technological advancements demonstrated by MAHLI enhance the capabilities of robotic exploration, paving the way for more sophisticated missions.