What's Happening?
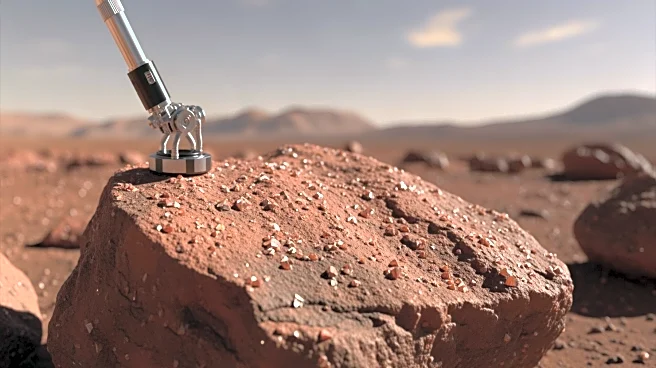
NASA's Curiosity Rover has achieved a significant milestone in its exploration of Mars by successfully analyzing organic compounds from the Nevado Sajama drill site. The rover's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM)
instrument utilized a gas chromatograph/mass spectrometer to detect carbon-containing materials, which are crucial for understanding Mars' potential to support life. This analysis marks a pivotal step in determining whether Mars' past environment could have been hospitable to life. The Curiosity team also completed a high-resolution 360-degree stereo mosaic of the drill site, using both wide-angle and telephoto Mastcam cameras, providing a comprehensive view of the Martian landscape. Additionally, the rover conducted nighttime imaging of the drill hole using its Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) with built-in LED lights, offering detailed insights into the drill hole's structure.
Why It's Important?
The detection of organic compounds on Mars is a groundbreaking development in astrobiology, as it provides essential clues about the planet's past habitability. Understanding the presence and composition of these compounds can help scientists determine if life ever existed on Mars. The high-resolution imaging and detailed analysis of the Martian surface contribute to a deeper understanding of the planet's geological history and environmental conditions. These findings could influence future Mars missions and the search for extraterrestrial life, potentially guiding the selection of landing sites and scientific objectives. The success of Curiosity's mission underscores the importance of continued investment in space exploration and the potential for discovering life beyond Earth.
What's Next?
Following the completion of its observations at Nevado Sajama, Curiosity is set to explore nearby areas identified by the science team for further data collection. The rover will continue its mission to gather crucial information about Mars' surface and subsurface, contributing to the broader understanding of the planet's history and potential for life. As the mission progresses, the team will likely focus on analyzing additional samples and conducting further imaging to build on the current findings. The ongoing exploration efforts will provide valuable insights that could shape future Mars exploration strategies and inform the development of new technologies for planetary research.