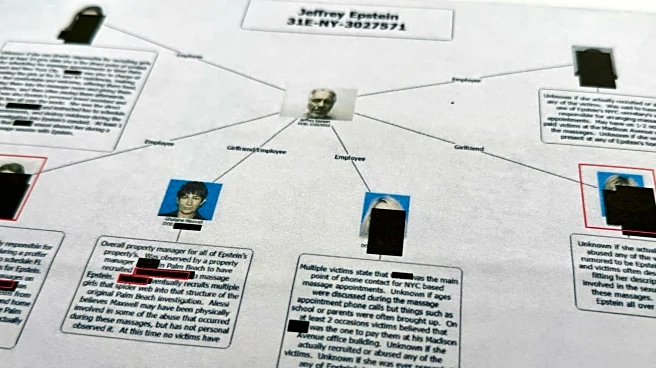
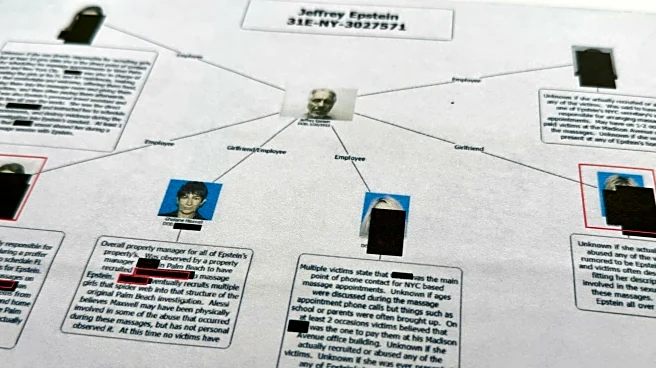
What's Happening?
A recent study has highlighted Texas as the leading state in the United States for fatal animal attacks, with 225 deaths reported between 2018 and 2023. The study, which analyzed data from the Centers for Disease Control, found a total of 1,604 animal-related
fatalities nationwide during this period. California and Florida followed Texas with 128 and 112 deaths, respectively. The Southern U.S. accounted for the highest percentage of these fatalities at 46.8%. The study noted that stings from hornets, wasps, and bees were responsible for 31% of the deaths, predominantly occurring in the Midwest. Additionally, dog attacks, which surged post-pandemic due to increased dog ownership during COVID-19 lockdowns, accounted for 26% of the fatalities. Other causes included encounters with venomous arthropods and marine animals.
Why It's Important?
The findings of this study underscore a significant public health concern, particularly in the Southern U.S., where the majority of these fatal encounters occur. The increase in dog attacks post-pandemic highlights the unintended consequences of lifestyle changes during COVID-19, such as more people working from home and acquiring pets. This trend necessitates increased public awareness and potentially new safety measures to mitigate risks associated with animal encounters. The data also suggests a need for targeted public health interventions in regions with high incidences of fatal stings and bites, to prevent further fatalities and educate the public on safety measures.
What's Next?
In response to these findings, public health officials may consider implementing educational campaigns focused on preventing animal attacks, particularly in high-risk areas like Texas and the Southern U.S. There could also be an emphasis on responsible pet ownership and safety practices to reduce the risk of dog attacks. Additionally, local governments might explore policies to manage and mitigate risks associated with venomous insects and other dangerous wildlife. Further research could be conducted to understand the underlying causes of these trends and develop more effective prevention strategies.