What's Happening?
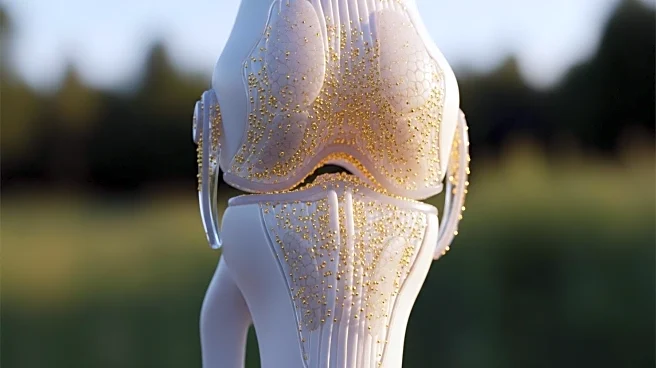
Recent research has demonstrated the potential of flexible tactile sensors based on gold nanoparticles-precipitated carbon nanotubes to monitor knee pressure and motion. These sensors, characterized by high sensitivity and low contact resistance, are designed to aid in biomechanical analysis and rehabilitation. The study involved attaching sensors to the knee and foot of subjects to measure walking motion in real-time, revealing significant changes in current signals corresponding to different states of movement. The sensors showed promise in detecting dynamic motion, which could be beneficial for real-time position monitoring and rehabilitation training.
Why It's Important?
The development of these sensors represents a significant advancement in the field of biomechanical monitoring and rehabilitation. By providing precise measurements of knee pressure and motion, these sensors could improve the diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as knee osteoarthritis and peripheral neuropathy. The ability to monitor real-time changes in pressure distribution can enhance physical therapy practices, offering more tailored and effective rehabilitation strategies. This technology could also lead to innovations in wearable healthcare devices, expanding their applications in monitoring various physiological pressures and movements.
What's Next?
The study suggests potential applications for these sensors in wearable healthcare devices, capable of detecting a wide range of pressures from subtle physiological signals to large-scale body motions. Future research may focus on optimizing sensor placement and improving signal-to-noise ratios to enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices. Additionally, the integration of these sensors into commercial healthcare products could revolutionize patient monitoring and rehabilitation, providing more comprehensive and real-time data for healthcare professionals.
Beyond the Headlines
The ethical implications of using advanced sensors in healthcare include concerns about data privacy and the potential for misuse of sensitive health information. As these technologies become more prevalent, establishing robust data protection measures will be crucial to ensure patient confidentiality and trust. Furthermore, the cultural acceptance of wearable health monitoring devices may vary, necessitating efforts to educate the public on their benefits and address any apprehensions.