What's Happening?
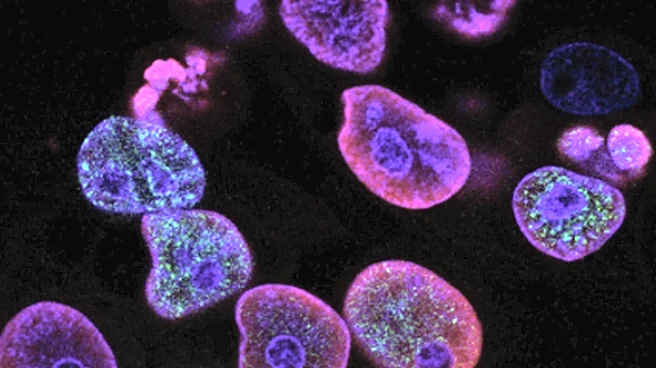
Recent advancements in cellular senescence research are paving the way for new clinical practices aimed at treating metabolic diseases. Cellular senescence, a state where cells cease to divide and secrete inflammatory factors, is linked to aging and various chronic diseases. Researchers are exploring senolytics, drugs that target and eliminate senescent cells, as potential treatments for conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Studies have shown that senolytics can improve physical function and increase lifespan by reducing the burden of senescent cells, which are associated with tissue damage and inflammation.
Why It's Important?
The translation of cellular senescence research into clinical practice could revolutionize the treatment of metabolic diseases, which are prevalent and costly to manage. By targeting the root causes of these conditions, such as senescent cells, healthcare providers can potentially offer more effective and sustainable treatments. This approach not only addresses symptoms but also targets underlying mechanisms, offering hope for improved healthspan and reduced healthcare costs. The development of senolytics could also lead to breakthroughs in treating other age-related diseases, enhancing overall quality of life.
What's Next?
The next steps involve conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of senolytic drugs in humans. Researchers are optimistic about the potential of these drugs to treat metabolic diseases and are exploring their application in other age-related conditions. Collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies will be crucial in advancing this research and bringing new treatments to market. Additionally, public health initiatives focused on lifestyle changes that complement senolytic therapy could further enhance treatment outcomes.
Beyond the Headlines
The ethical implications of targeting senescent cells raise important questions about the balance between extending lifespan and maintaining quality of life. As research progresses, it will be essential to consider the long-term effects of senolytic treatments and their impact on aging populations. Furthermore, understanding the role of cellular senescence in different tissues could lead to personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatments to individual needs and conditions.