What's Happening?
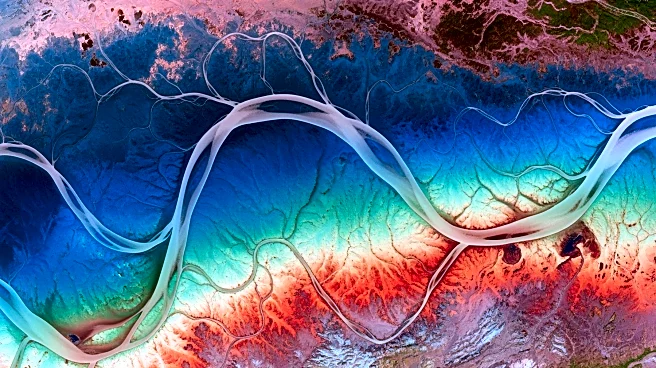
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission has released a new image showcasing its ability to penetrate clouds and reveal detailed surface characteristics of the Mississippi River Delta in Louisiana.
The satellite, equipped with an L-band radar, captures data that can distinguish between different types of land cover, such as vegetation, urban structures, and water bodies. This capability is crucial for monitoring environmental changes, including forest and wetland ecosystems, and agricultural developments. The mission, a collaboration between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, aims to provide comprehensive data for various applications, including disaster response and infrastructure monitoring.
Why It's Important?
The NISAR mission represents a significant advancement in Earth observation technology, offering detailed insights into environmental and infrastructural changes. By providing high-resolution data, the mission supports efforts in disaster management, agricultural planning, and environmental conservation. The ability to monitor land and ice surfaces with precision can aid in addressing climate change impacts and improving resource management. This collaboration between NASA and ISRO also highlights the importance of international partnerships in advancing scientific research and technological innovation.
What's Next?
As the NISAR mission continues, it will release thousands of data files for public access, enabling researchers and policymakers to utilize this information for various applications. The mission's ongoing data collection will enhance understanding of global environmental changes and support decision-making processes in areas such as urban planning, agriculture, and disaster preparedness. The success of NISAR could lead to further collaborations between international space agencies, fostering advancements in satellite technology and Earth observation capabilities.