What's Happening?
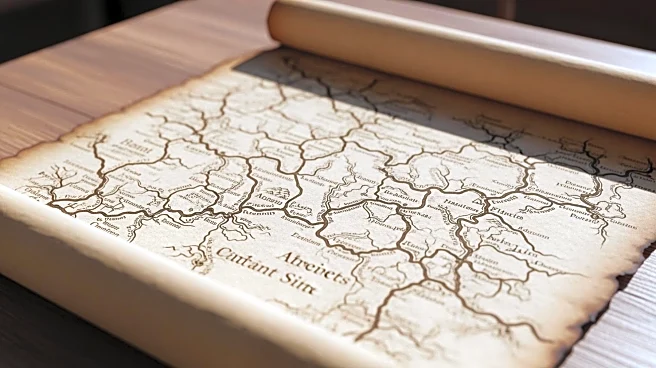
A recent study has unveiled a high-resolution dataset detailing the road networks of the Roman Empire, providing significant insights into ancient infrastructure. The dataset, named Itiner-e, was developed
through a comprehensive digitization process that involved identifying roads using historical and archaeological sources, modern and historical aerial photographs, and satellite imagery. The study focused on the Roman Empire's road system during the Antonine dynasty, around 150 CE, when the empire reached its largest extent. The dataset includes information on road segments, milestones, and ancient sites, offering a detailed view of the Roman road network across various regions, including North Africa, the Near East, Asia Minor, and Europe. The project was a collaborative effort between multiple research initiatives, including MINERVA and Viator-e, and aimed to improve spatial accuracy and coverage compared to previous datasets.
Why It's Important?
The creation of this high-resolution dataset is crucial for understanding the Roman Empire's infrastructure and its impact on trade, communication, and military logistics. By providing detailed information on road networks, the dataset allows historians and archaeologists to better analyze the economic and social dynamics of ancient Rome. The roads facilitated the movement of goods, people, and armies, playing a vital role in the empire's expansion and administration. This dataset can also aid in the preservation of archaeological sites and inform modern infrastructure projects by highlighting historical routes that may still influence contemporary road systems. The enhanced spatial accuracy and coverage offer a more comprehensive view of the Roman Empire's reach and connectivity, contributing to the broader field of historical geography.
What's Next?
The dataset is expected to be used in further research to explore the evolution of the Roman road system over time and its influence on subsequent infrastructure developments. Researchers may focus on comparing the infrastructure investments of different Roman emperors and examining the integration of pre-Roman roads into the Roman network. The dataset also opens opportunities for interdisciplinary studies, combining historical geography with modern technology to model ancient transportation networks. Future projects may expand the dataset to include more regions or refine existing data with new archaeological findings, enhancing our understanding of ancient civilizations and their legacies.
Beyond the Headlines
The dataset not only provides historical insights but also raises questions about the ethical considerations of preserving ancient infrastructure in modern times. As urban development encroaches on historical sites, balancing preservation with progress becomes a critical issue. The study highlights the importance of using technology to safeguard cultural heritage while accommodating contemporary needs. Additionally, the dataset underscores the interconnectedness of ancient societies, offering lessons on the importance of infrastructure in fostering economic and cultural exchange.