What is the story about?
What's Happening?
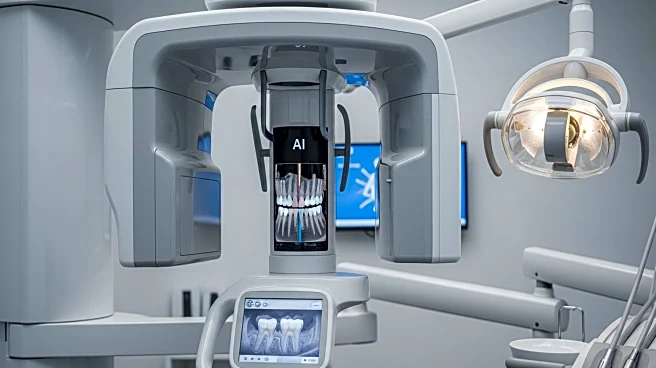
A new dataset, DenPAR, has been introduced to improve the diagnosis of dental diseases using artificial intelligence. The dataset consists of 1000 intra-oral periapical (IOPA) radiographs, which are crucial for diagnosing various dental conditions. These radiographs are annotated with important landmarks such as tooth segmentation masks, Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ) points, apex points, and alveolar crestal bone levels. The dataset aims to facilitate the development of machine learning and deep learning models that can automatically detect dental diseases, thus enhancing early diagnosis and treatment outcomes. The use of AI in analyzing these radiographs could significantly assist dentists by reducing errors and improving the accuracy of diagnoses.
Why It's Important?
The introduction of the DenPAR dataset is significant as it addresses the growing need for efficient and accurate dental disease diagnosis. Dental diseases are a major public health concern, affecting billions globally. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent complications such as tooth loss and pain. By leveraging AI, the dataset could revolutionize dental diagnostics, making it more accessible and cost-effective. This advancement could lead to better patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare systems. The dataset's potential to improve clinical practice and research in dentistry highlights its importance in the field.
What's Next?
The next steps involve utilizing the DenPAR dataset to train various AI models for dental diagnostics. These models could include teeth segmentation, keypoint detection, and alveolar bone level identification. The development of advanced clinical decision support systems using this dataset could further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of dental diagnoses. Researchers and healthcare professionals may focus on integrating these AI-driven solutions into routine dental practice, potentially transforming the landscape of dental care.