What's Happening?
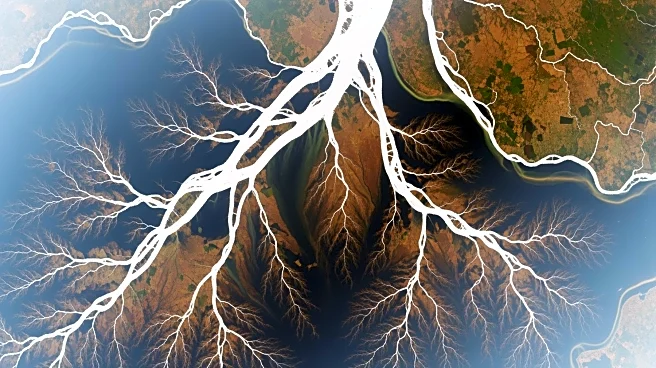
NASA, in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), has released a new radar image of the Mississippi River Delta using data from the NISAR satellite. This joint Earth-observation mission utilizes synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
to capture images that penetrate cloud cover, providing detailed insights into the region's topography and vegetation. The image, acquired on November 29, 2025, highlights the Mississippi Delta's complex landscape, including wetlands, forests, and urban areas, which are often obscured in optical satellite images due to cloud cover. The NISAR mission combines two SAR instruments with different wavelengths, allowing for comprehensive monitoring of environmental changes, such as shoreline shifts and vegetation health. This capability is crucial for tracking gradual changes that impact local communities and infrastructure.
Why It's Important?
The NISAR satellite's ability to provide consistent, cloud-penetrating imagery is significant for environmental monitoring and public policy. The Mississippi Delta is a dynamic and vulnerable region, with changes in its landscape directly affecting local economies and infrastructure. Satellite data can inform decisions on levee reinforcement, coastal restoration, and flood risk management. The mission's dual-band radar system enhances the precision of environmental assessments, offering valuable data for scientists, government agencies, and local communities. This information is essential for understanding and mitigating the impacts of land subsidence, erosion, and sea-level rise, which threaten the region's ecological and economic stability.
What's Next?
The NISAR mission is preparing for a broader release of data by February 2026, allowing a wide range of users to access and utilize the information for various applications. This includes universities, government agencies, and private sector entities involved in risk management and infrastructure monitoring. The continuous data stream from NISAR will enable more precise and timely environmental assessments, supporting efforts to address the challenges posed by climate change and land degradation. As the mission progresses, it is expected to become a critical tool for global environmental monitoring, providing insights into changes across diverse ecosystems and landscapes.