What's Happening?
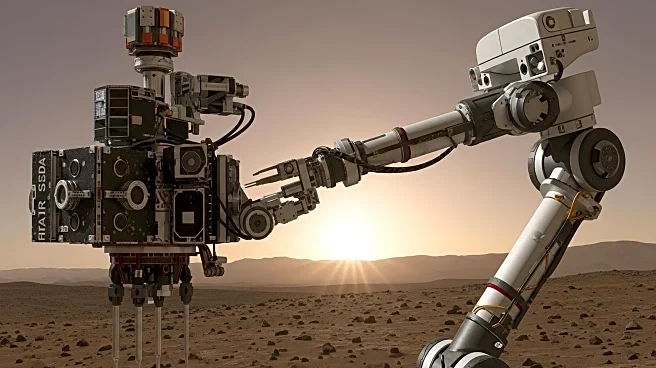
NASA's Perseverance rover, equipped with the SHERLOC instrument, is advancing the exploration of Mars by utilizing spectroscopy to analyze the planet's surface. SHERLOC, which stands for Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals, is a Raman spectroscopy tool that helps identify organic compounds and assess Mars' past habitability. The instrument is mounted on the rover's robotic arm and uses a high-powered laser to conduct precise spectroscopic analysis of Martian rocks and soil. This technology allows scientists to detect minerals and potential biosignatures, contributing to the understanding of Mars' geological diversity and environmental history.
Why It's Important?
The use of SHERLOC in Mars exploration is significant as it enhances the ability to detect signs of past or present life on the planet. By identifying organic molecules and minerals, SHERLOC provides insights into Mars' habitability and the potential for life beyond Earth. The findings from SHERLOC's analysis can inform future missions and the search for extraterrestrial life. Additionally, the instrument's ability to perform detailed spectroscopic analysis supports the broader Mars Sample Return mission, which aims to bring samples back to Earth for further study. This advancement in planetary exploration technology underscores the importance of spectroscopy in astrobiology and the quest to understand the universe.
What's Next?
SHERLOC will continue to play a crucial role in collecting samples from Mars, with plans to return these samples to Earth by 2030 as part of the Mars Sample Return mission. The ongoing development of spectroscopy techniques and instruments will likely enhance the accuracy and efficiency of space exploration. Researchers are also working on miniaturized spectroscopy systems that could reduce payload weight and fuel consumption for future missions. As investment in advanced imaging technologies grows, we can expect more intelligent and compact systems to be used in the search for life on distant planets and in studying cosmic phenomena.