What's Happening?
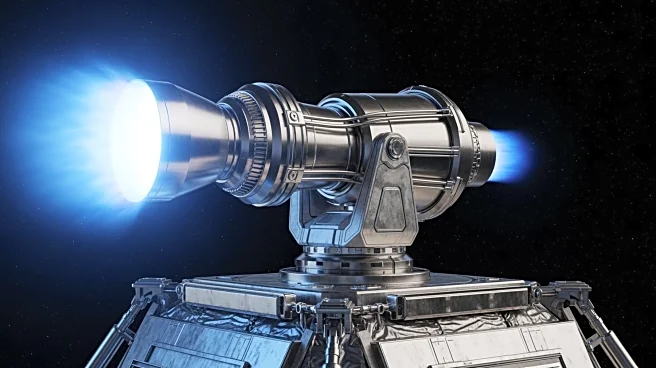
NASA has installed three 12-kilowatt electric thrusters on its lunar Gateway station, marking a significant advancement in space propulsion technology. Developed by L3Harris Technologies, these thrusters are part of the Advanced Electric Propulsion System
(AEPS) and are the most powerful electric propulsion systems ever sent into space. The thrusters completed hot-fire testing at NASA's Glenn Research Center and are now integrated into the Power and Propulsion Element of the Gateway. This development is crucial for NASA's Artemis IV mission, which aims to establish a human presence around the Moon. The Gateway will serve as a staging post for astronauts heading to the lunar surface and beyond, supporting scientific missions and future deep space exploration.
Why It's Important?
The installation of these advanced thrusters is a pivotal step in NASA's Artemis program, which seeks to return humans to the Moon and eventually send them to Mars. The electric propulsion system offers significantly higher fuel efficiency compared to traditional chemical engines, allowing for longer missions and the transportation of heavier payloads. This technology not only supports lunar exploration but also opens possibilities for missions to distant destinations like Jupiter's moons or Mars. The Gateway's success is integral to the Artemis missions, as it will facilitate crew transfers and logistics, playing a key role in NASA's long-term space exploration goals.
What's Next?
As the Gateway station moves closer to operational status, NASA will continue to collaborate with commercial and international partners to ensure its success. The station's development will be closely monitored, with further testing and integration of systems expected. The Artemis IV mission, which will utilize the Gateway, is a critical component of NASA's strategy to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Future missions may also explore the potential of pairing the AEPS with nuclear power sources, further expanding the scope of space exploration.