What's Happening?
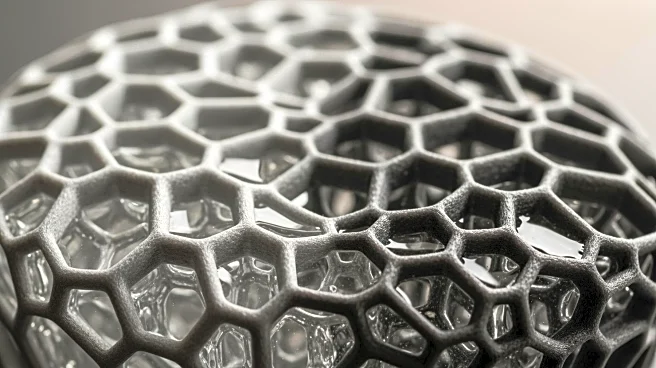
A recent study published in Nature explores the mechanical resilience of 3D-printed structures with soft-hard bicontinuous nanostructures. The research focuses on the impact of epoxy infiltration on porous
and solid 3D-printed architectures. The study reveals that porous structures, when infiltrated with epoxy, exhibit significant improvements in mechanical performance, including compressive strength, elastic modulus, and toughness. The porous architecture allows deep resin infiltration, enhancing load distribution and energy absorption. In contrast, solid structures show limited improvement due to epoxy coating remaining on the surface without penetrating the internal matrix. The findings highlight the effectiveness of phase-separated interpenetrating composites (IPC) in optimizing mechanical reinforcement.
Why It's Important?
The study's findings have significant implications for industries relying on 3D printing technology, such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. Enhanced mechanical performance in 3D-printed structures can lead to more durable and reliable components, reducing material costs and increasing efficiency. The ability to improve load distribution and energy absorption through epoxy infiltration could revolutionize the design and manufacturing processes, offering new opportunities for innovation in structural engineering. Companies and researchers in the U.S. may benefit from adopting these advanced techniques to enhance product quality and performance.
What's Next?
Future research may focus on optimizing the epoxy infiltration process for various 3D-printed geometries and materials. Stakeholders in the manufacturing and engineering sectors might explore the application of these findings to develop new products with improved mechanical properties. Additionally, collaborations between academic institutions and industry leaders could drive further advancements in 3D printing technology, potentially leading to the development of new standards and practices for structural design and reinforcement.
Beyond the Headlines
The study raises ethical considerations regarding the environmental impact of increased epoxy use in manufacturing. As industries adopt these techniques, there may be a need to address sustainability and waste management issues associated with epoxy materials. Furthermore, the research highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing technology, combining insights from materials science, engineering, and manufacturing to achieve breakthroughs in structural design.