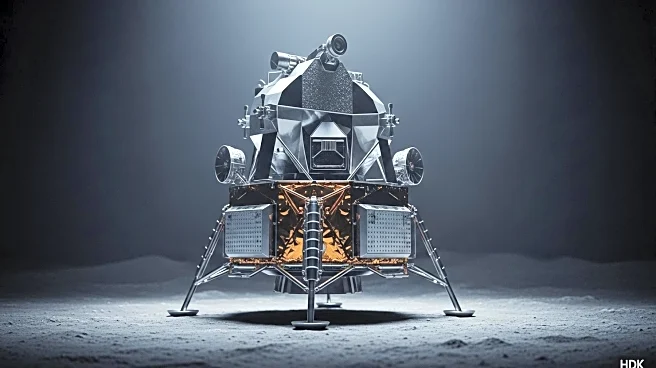
What's Happening?
China's space program has achieved a significant milestone with the successful testing of its two-person lunar lander, named 'Lanyue,' on August 6. The test involved a simulated takeoff and landing at a specialized site in Hebei Province, validating the lander's critical systems for touchdown and ascent. This development is part of China's broader lunar mission architecture, which includes successful tests of the Mengzhou crewed spacecraft and the first-stage propulsion system for its new-generation Long March 10 rocket. The China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) has stated that Lanyue will serve as a 'lunar life center, energy center, and data center' for astronauts, supporting lunar residence and activities.
Why It's Important?
The successful test of the Lanyue lunar lander marks a crucial step in China's ambitious program to send astronauts to the moon. This advancement demonstrates China's growing capabilities in space exploration and its commitment to establishing a human presence on the lunar surface. The development of the lunar lander, along with other components of the lunar mission architecture, positions China as a significant player in the global space race. The implications for U.S. industries and public policy could include increased competition in space technology and exploration, potentially influencing international collaborations and funding priorities.
What's Next?
China's space program is expected to continue its methodical progress towards a crewed lunar landing. Future steps may include further testing of the Long March 10 rocket and the Mengzhou crewed spacecraft, as well as preparations for the actual lunar mission. The international space community will likely monitor these developments closely, as China's advancements could impact global space exploration strategies and partnerships.
Beyond the Headlines
China's lunar mission reflects broader geopolitical ambitions and technological advancements. The successful tests underscore China's commitment to becoming a leader in space exploration, which may influence global perceptions of technological prowess and innovation. Additionally, the development of lunar infrastructure could have long-term implications for scientific research and resource utilization on the moon.