What's Happening?
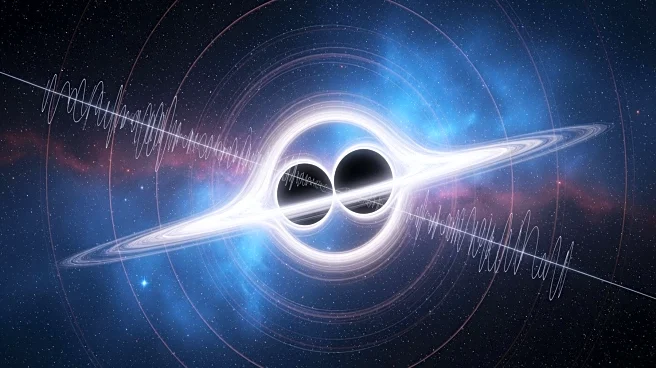
A recent cosmic event involving the collision of two black holes has confirmed predictions made by Stephen Hawking and Albert Einstein. Observations from gravitational wave observatories validated Hawking's
area theorem, showing an increase in the surface area of the resulting black hole, and matched Einstein's predictions regarding the black hole's ring down, revealing a new Kerr black hole. Additionally, moss spores exposed to space conditions on the International Space Station for nine months successfully germinated upon return to Earth, supporting theories like panspermia. The Excalibur mission is also advancing astronomy by using a balloon-based telescope to measure X-ray polarization from cosmic objects.
Why It's Important?
The confirmation of Hawking and Einstein's theories through black hole collision observations is a significant milestone in astrophysics, providing deeper insights into the nature of black holes and the universe. The resilience of moss spores in space supports the possibility of life's building blocks surviving interplanetary journeys, potentially influencing theories about the origin of life. The Excalibur mission's innovative approach to astronomy could lead to new discoveries about cosmic magnetic fields and structures, enhancing our understanding of the universe. These developments collectively push the boundaries of space research and exploration.
What's Next?
Future research will likely focus on further validating and expanding upon the findings from the black hole collision, potentially leading to new theoretical advancements in astrophysics. The resilience of extremophiles like moss spores may prompt additional studies on the potential for life to survive in space, influencing astrobiology and the search for extraterrestrial life. The success of the Excalibur mission may encourage more balloon-based astronomy projects, offering a cost-effective method for observing cosmic phenomena. These initiatives could drive new collaborations and technological innovations in space exploration.