What's Happening?
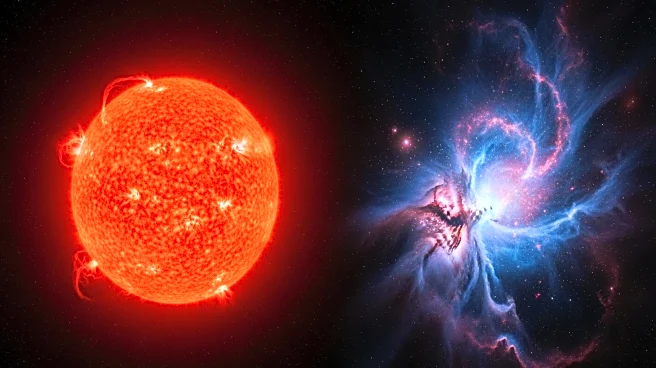
The dimming of Betelgeuse in 2019 sparked speculation about its potential explosion as a supernova. Although it hasn't exploded yet, its fate can be previewed by observing the nearby Crab Nebula. Betelgeuse,
a supergiant star in Orion, is known for its massive size and rapid life cycle. It has exhausted its hydrogen fuel and is now fusing helium, causing it to swell. The Crab Nebula, located in Taurus, is the remnant of a supernova observed in 1054. It contains a rapidly spinning neutron star, the last remnant of the explosion. The nebula's gas clouds, rich in elements like silicon and iron, are essential for forming rocky planets like Earth.
Why It's Important?
Studying Betelgeuse and the Crab Nebula provides valuable insights into the life cycles of stars and the processes that lead to supernovae. These events play a crucial role in enriching the universe with heavy elements necessary for planet formation. Understanding these processes helps scientists learn more about the origins of our solar system and the conditions that make life possible. The observations of Betelgeuse and the Crab Nebula contribute to our knowledge of stellar evolution and the dynamic nature of the cosmos.
What's Next?
Astronomers will continue to monitor Betelgeuse for signs of an impending supernova, while the Crab Nebula remains a subject of study for its unique characteristics. Future observations will focus on understanding the mechanisms behind supernovae and the distribution of elements in the universe. These studies will enhance our comprehension of cosmic events and their impact on the formation of planetary systems.