What is the story about?
What's Happening?
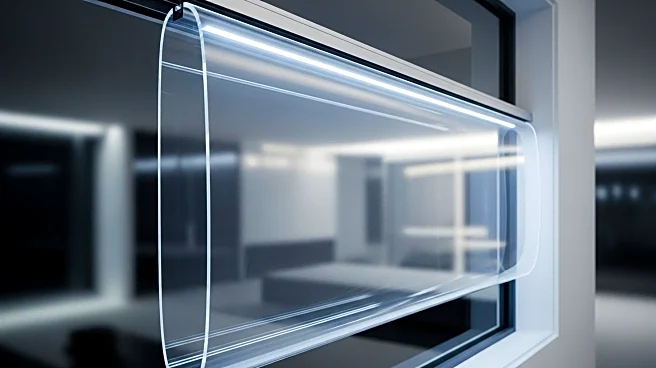
Researchers have introduced a new type of smart window that integrates multiple functionalities such as optical tuning, thermal control, and self-cleaning capabilities. This innovation aims to address energy inefficiencies associated with traditional glass windows, which contribute to significant energy loss in buildings. The smart window utilizes a self-cleaning electro-thermal actuated (SETA) device, combining a thermo-responsive hydrogel with a hydrophobic silver nanowire heater. This design allows for precise control over light transmission, low power consumption, and easy cleaning, making it suitable for both flat and curved surfaces.
Why It's Important?
The development of this multifunctional smart window represents a significant advancement in sustainable building materials. By integrating features like optical regulation, thermal management, and self-cleaning, the window addresses key limitations of conventional smart windows. Its potential applications in greenhouses, intelligent vehicles, and architectural facades highlight its transformative potential in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability. The technology could lead to reduced energy consumption in buildings, contributing to broader environmental goals.
What's Next?
Further research and development are needed to address the scratch resistance of the smart window before it can be widely adopted in harsher environments. The scalability and multifunctional integration of the technology suggest a promising future for its application in various industries. As the technology matures, it could play a crucial role in advancing sustainable infrastructure and energy-efficient building practices.