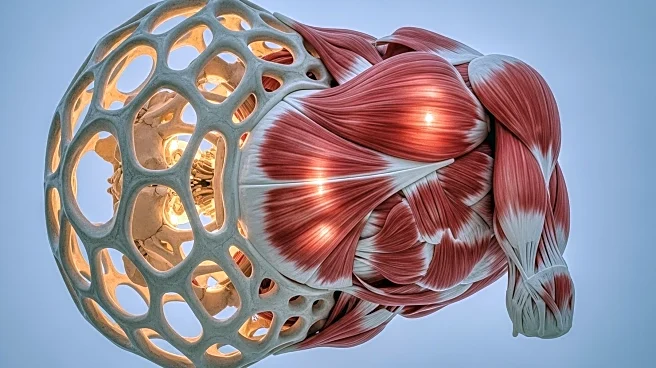
What's Happening?
Researchers at ETH Zurich's Soft Robotics Lab have developed a biohybrid system that replicates the interface between bones and muscles, enhancing force transmission. This innovation combines synthetic and biological materials to mimic the structure and function of biological tissues, potentially advancing medical implants and robotics. The system uses a 3D bioprinted actuator that mimics the natural connection between muscle and bone, creating a functional model of tendons and their transition to muscle. This breakthrough could lead to biohybrid robots and implants that improve human-machine interaction in healthcare and assistive robotics.
Why It's Important?
The development of biohybrid systems represents a significant advancement in both robotics and medical technology. By mimicking the natural musculoskeletal system, this innovation could lead to more effective and integrated medical implants, potentially improving patient outcomes in areas such as prosthetics and regenerative medicine. Additionally, the ability to replicate biological interfaces in robotics could enhance the precision and functionality of robotic systems, offering new possibilities in healthcare and assistive technologies. This research underscores the potential for interdisciplinary collaboration to drive technological and medical advancements.
What's Next?
Future applications of this biohybrid system could include adaptive prosthetics and biologically integrated robotic systems. Researchers may focus on refining the technology for specific medical applications, such as modeling the middle ear's biomechanics or developing lab-grown replacement tissues. Continued research and development could lead to commercial applications, enhancing the integration of biological and synthetic materials in medical and robotic fields.
Beyond the Headlines
The ethical implications of integrating biological tissues with robotics could spark discussions on the boundaries between human and machine. As biohybrid systems become more prevalent, considerations around the long-term effects on human health and the potential for creating semi-autonomous systems may arise. This development could also influence cultural perceptions of technology's role in healthcare.