What's Happening?
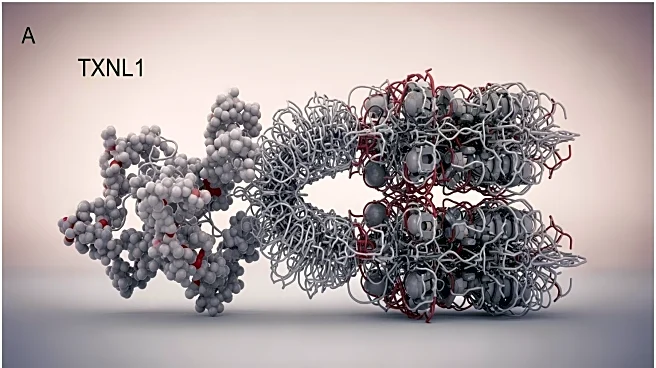
A recent study has provided insights into the structural dynamics of the 26S proteasome, focusing on the binding of the thioredoxin-like protein TXNL1. Using cryo-electron microscopy, researchers identified TXNL1's interaction with the proteasome during
substrate degradation. The study revealed that TXNL1 binds to the proteasome in a conformation-specific manner, coordinating with the active-site zinc of Rpn11, a component of the proteasome. The research highlights the complex interactions within the proteasome that facilitate protein degradation, a critical cellular process.
Why It's Important?
Understanding the structural dynamics of the 26S proteasome is crucial for insights into cellular protein degradation, which is vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis. The findings about TXNL1's role could have implications for developing therapeutic strategies targeting proteasome function, particularly in diseases where protein degradation is disrupted, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. The study enhances the understanding of proteasome regulation and its potential as a drug target.
What's Next?
Further research is needed to explore the functional implications of TXNL1's interaction with the proteasome. Investigating how these interactions affect proteasome activity in different cellular contexts could provide deeper insights into their biological significance. Additionally, exploring the potential for targeting TXNL1-proteasome interactions in therapeutic applications could be a promising avenue for future studies.
Beyond the Headlines
The study underscores the importance of structural biology in unraveling complex protein interactions. It also highlights the potential for using advanced imaging techniques like cryo-electron microscopy to gain detailed insights into molecular mechanisms. These findings contribute to the broader understanding of cellular processes and their implications for health and disease.