What is the story about?
What's Happening?
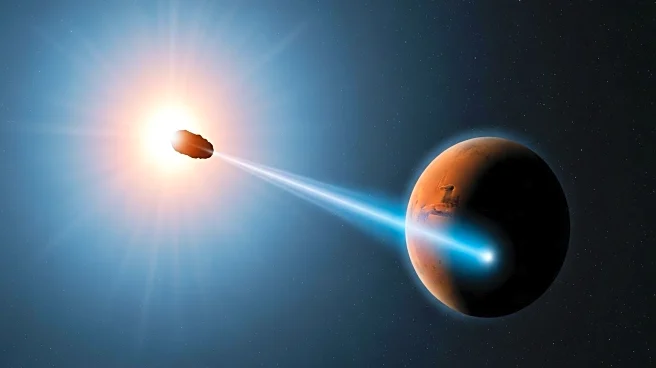
The interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, believed to be a comet, is traveling through the solar system at 137,000 miles per hour and is set to pass close to Mars. Recently, a coronal mass ejection from the Sun collided with 3I/ATLAS, raising questions about the effects of solar radiation on interstellar objects. Observations have revealed a higher carbon dioxide to water ratio in the comet, adding to the mystery of its composition. Scientists are eager to study the impact of the solar event as the comet approaches Mars.
Why It's Important?
The interaction between 3I/ATLAS and the Sun's coronal mass ejection presents a unique opportunity to study the effects of solar phenomena on interstellar objects. Understanding these interactions can provide valuable data on the behavior and characteristics of such objects, which are crucial for advancing knowledge in space exploration and astrophysics. The comet's unusual composition and trajectory offer insights into the diversity of celestial bodies and the potential for discovering new cosmic phenomena.
What's Next?
As 3I/ATLAS nears Mars, scientists will continue to monitor its trajectory and physical characteristics. The comet's close approach to Mars provides an opportunity for further observation and data collection, which could enhance understanding of interstellar objects and their interactions with solar phenomena. Researchers are particularly interested in the comet's brightening and gas emissions, which may reveal more about its composition and behavior.