What's Happening?
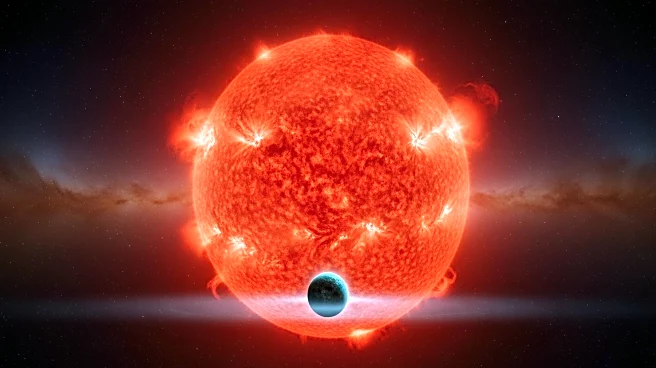
Scientists have discovered a strip of iron in the Ring Nebula, which may be the remains of a planet destroyed by a dying star. This finding, published in Oxford Academic, suggests a possible future for Earth
when the Sun eventually expands into a red giant. The study utilized the Large Integral Field Unit (LIFU) to scan the nebula, revealing the iron bar. Experts speculate that this could be a preview of Earth's fate in about five billion years when the Sun's outer layers expand, potentially vaporizing the planet. The discovery provides insights into the life cycle of stars and the potential end of rocky planets like Earth.
Why It's Important?
The study highlights the long-term fate of Earth and similar planets as their stars evolve. Understanding this process is crucial for astronomers studying the life cycles of stars and the potential for planetary survival. The findings could influence future research on planetary systems and the conditions necessary for planets to endure the death of their stars. This knowledge is significant for the scientific community as it seeks to understand the broader dynamics of the universe and the eventual fate of our solar system.
What's Next?
Further research is needed to confirm whether the iron bar in the Ring Nebula is indeed the remains of a planet. Scientists aim to find similar structures in other nebulae to piece together the puzzle of planetary destruction and survival. This ongoing research could provide more clues about the future of Earth and other planets in similar systems, enhancing our understanding of cosmic evolution.
Beyond the Headlines
The discovery raises questions about the long-term sustainability of life on Earth and the potential for human survival beyond our planet. As scientists explore the universe, understanding the limits of planetary survival could inform future space exploration and the search for habitable worlds. The study also underscores the importance of preserving Earth's environment, as it highlights the inevitable changes our planet will face in the distant future.