What's Happening?
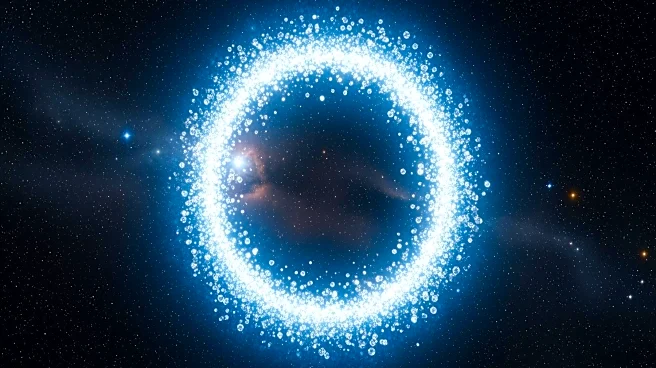
NASA's Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) has captured a striking image of a cosmic formation known as the 'diamond ring' located 4,500 light-years away in the Cygnus constellation. This formation is an expanding gas bubble of ionized
carbon, created by the intense radiation and stellar winds of a hot, massive star. The ring, about 20 light-years across, is the remnant of a burst bubble that expanded within a flat molecular cloud before rupturing. The image reveals a circular loop with a bright clump on one side, initially thought to be part of the ring but later identified as a separate object aligned by chance. The SOFIA observatory, a 2.7-meter telescope mounted on a Boeing 747SP aircraft, flew at an altitude of 45,000 feet to capture infrared wavelengths invisible to ground-based observatories. Although SOFIA was canceled in September 2022 due to budget constraints, its archive continues to provide valuable data for astronomers.
Why It's Important?
The discovery of the 'diamond ring' formation offers significant insights into the processes of star formation and the influence of massive stars on their surrounding environments. Understanding these processes is crucial for comprehending the formation of stars in the Milky Way. The ability of individual stars to affect large cloud complexes highlights the dynamic nature of stellar evolution and the complex interactions within star-forming regions. The continued analysis of SOFIA's infrared observations, despite the observatory's cancellation, underscores the importance of archival data in advancing astronomical research. This discovery not only enriches our understanding of cosmic phenomena but also demonstrates the enduring impact of past scientific missions.
What's Next?
Astronomers will continue to analyze the vast archive of infrared observations collected by SOFIA to uncover more about the formation and evolution of stars and their impact on surrounding molecular clouds. Further studies may focus on the detailed dynamics of the 'diamond ring' and similar formations to better understand the lifecycle of massive stars and their role in shaping the cosmos. Collaborative efforts among international research teams could lead to new discoveries and enhance our knowledge of the universe's complex structures.
Beyond the Headlines
The 'diamond ring' formation serves as a reminder of the intricate and often unexpected phenomena occurring in the universe. The alignment of the bright clump with the ring, purely by chance, illustrates the complexity of cosmic observations and the importance of perspective in astronomical studies. This discovery also highlights the role of advanced technology, such as airborne observatories, in overcoming atmospheric limitations and expanding our view of the universe. The continued exploration of SOFIA's data may reveal more about the interplay between stars and their environments, offering deeper insights into the fundamental processes driving cosmic evolution.