What is the story about?
What's Happening?
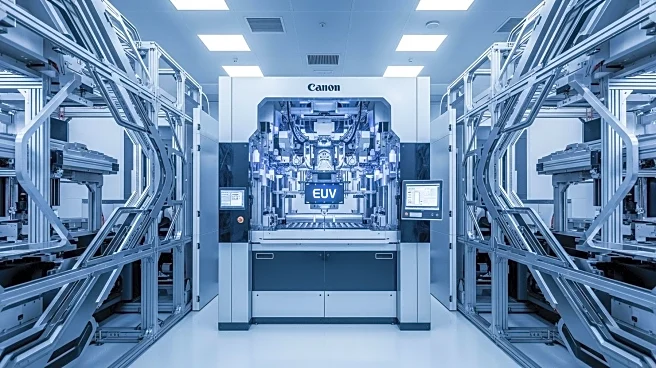
SK hynix has announced the deployment of the world's first High Numerical Aperture Extreme Ultraviolet (High NA EUV) lithography machine for mass production at its M16 fab in Icheon, South Korea. This advanced TWINSCAN EXE:5200B system is set to produce cutting-edge DRAM chips with transistors 1.7 times smaller and 2.9 times denser than previous models. The machine offers a 40% improvement in numerical aperture, enhancing the company's ability to manufacture powerful memory chips at reduced costs. SK hynix aims to leverage this technology to strengthen its position in the AI computing market, which is increasingly demanding high-performance memory solutions.
Why It's Important?
The introduction of High NA EUV technology by SK hynix marks a significant advancement in semiconductor manufacturing, potentially reshaping the competitive landscape. This development is crucial for industries reliant on high-performance computing, such as AI and next-generation computing markets. By improving chip density and reducing production costs, SK hynix could gain a competitive edge over rivals like Intel, impacting global supply chains and pricing strategies. The move also underscores the growing importance of AI-driven applications, which require increasingly sophisticated memory solutions.
What's Next?
SK hynix plans to focus on mass production of advanced DRAM chips, targeting AI data centers as primary beneficiaries. The company aims to enhance its leadership in the AI memory space, potentially influencing market dynamics and prompting competitors to accelerate their own technological advancements. As the demand for AI and computing power continues to rise, SK hynix's strategic deployment of High NA EUV technology may drive further innovation and investment in semiconductor manufacturing.
Beyond the Headlines
The deployment of High NA EUV technology raises questions about the future of semiconductor manufacturing and its environmental impact. As companies strive for smaller, more efficient chips, the industry must balance technological progress with sustainable practices. Additionally, the geopolitical implications of advanced manufacturing capabilities in South Korea could affect international trade relations and technology sharing agreements.