What's Happening?
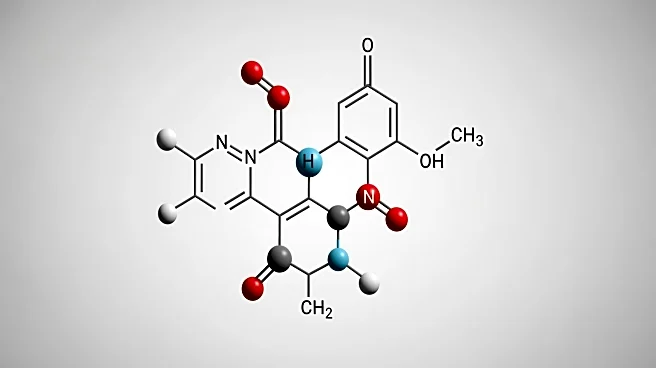
A new study has introduced a pyridine-thiazole hybrid adsorbent, MPHT 4, which has demonstrated significant efficiency in removing methylene blue (MB) from water. The adsorbent was synthesized through a one-pot reaction involving pyridine carbaldehyde,
thiosemicarbazide, and phenacyl bromide. Characterization of MPHT 4 revealed a homogeneous morphology with a surface area of 68.83 m²/g and micropore-dominated porosity, which facilitates effective dye adsorption. Under optimized conditions, the adsorbent achieved an 86.7% removal rate of MB. The study also explored the adsorption kinetics, revealing that the process follows a pseudo-second-order model, indicating that physisorption, likely involving electrostatic interactions, governs the adsorption process.
Why It's Important?
The development of MPHT 4 as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue removal is significant for wastewater treatment applications. Methylene blue is a common pollutant in industrial wastewater, and its effective removal is crucial for environmental protection. The high removal efficiency of MPHT 4 suggests it could be a valuable tool for industries seeking to reduce their environmental impact. The study's findings also highlight the potential for using similar hybrid adsorbents in other applications, potentially leading to advancements in water purification technologies. This could benefit industries by providing a cost-effective and efficient method for dye removal, thereby supporting regulatory compliance and sustainability goals.
What's Next?
Further research could explore the scalability of MPHT 4 production and its application in real-world wastewater treatment scenarios. Additionally, investigating the adsorbent's performance with other pollutants could expand its utility. Industries and environmental agencies may take interest in these findings, potentially leading to collaborations for developing commercial applications. The study also opens avenues for exploring other hybrid materials with similar or enhanced properties, which could lead to broader applications in environmental remediation.
Beyond the Headlines
The study of MPHT 4 not only addresses immediate environmental concerns but also contributes to the broader field of materials science. The synthesis and characterization of such hybrid materials could inspire further research into multifunctional adsorbents. This could lead to innovations in various fields, including catalysis and sensor technology, where similar materials might be applied. The environmental and economic implications of such advancements could be profound, promoting sustainable practices across multiple sectors.