What's Happening?
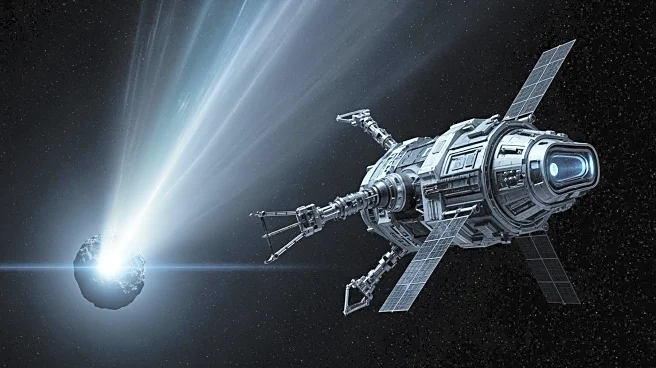
Meteorologists and astronomers are preparing to gather data from Comet 3I/ATLAS's tail using the Europa Clipper spacecraft. The alignment of the sun, Europa Clipper, and the comet between October 30 and November
6, 2025, presents a unique opportunity to sample charged particles from the comet's ion tail. This interaction is expected to provide insights into the composition of interstellar comets and the star systems that formed them. The study, detailed on arXiv, highlights the potential for Europa Clipper to collect data without damage, offering a rare chance to study an object from beyond the solar system.
Why It's Important?
Sampling the tail of Comet 3I/ATLAS is crucial for understanding the composition and origins of interstellar comets, which remain largely mysterious. This research could expand knowledge about the cosmos beyond the solar system, providing data on the interior of such comets and the star systems they originate from. The findings may enhance scientific understanding of galactic processes and contribute to the broader field of astronomy. Successful data collection could pave the way for future missions targeting interstellar objects, advancing space exploration and our understanding of the universe.
What's Next?
Researchers are coordinating with mission controllers to ensure the necessary instruments on Europa Clipper are activated in time to sample the comet's tail. The spacecraft's plasma instrument and magnetometer are crucial for analyzing the ions and magnetic effects. The success of this mission depends on precise alignment and functioning of the spacecraft's systems. If successful, this will mark the first time particles from an interstellar comet are collected, potentially leading to new discoveries about the galaxy.
Beyond the Headlines
The mission highlights the challenges and opportunities in space exploration, emphasizing the need for advanced technology and international collaboration. The study of interstellar comets could lead to breakthroughs in understanding the universe's formation and evolution, offering insights into the building blocks of life and the potential for habitable environments beyond Earth.