What is the story about?
What's Happening?
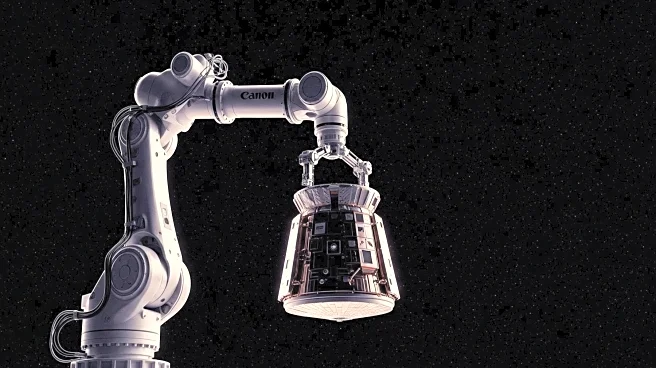
NASA is currently overseeing the installation of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus XL spacecraft onto the International Space Station (ISS). The operation involves the use of the Canadarm2 robotic arm, which was operated by NASA astronaut Jonny Kim, with Zena Cardman as backup. The Cygnus XL, launched on September 14 from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, is delivering over 11,000 pounds of scientific investigations and cargo to the ISS. The spacecraft will remain attached to the station until March 2026, after which it will depart and dispose of several thousand pounds of trash by burning up during re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
Why It's Important?
The successful installation of Cygnus XL is crucial for ongoing scientific research and operations aboard the ISS. The cargo includes vital scientific investigations that will contribute to various research fields, potentially leading to advancements in space exploration and technology. The operation also highlights the collaboration between NASA and private companies like Northrop Grumman, showcasing the role of commercial entities in supporting space missions. This partnership is essential for the sustainability and expansion of space exploration efforts, which can have significant implications for technological innovation and international cooperation.
What's Next?
Cygnus XL will remain at the ISS until March 2026, providing a platform for scientific experiments and research. During this period, the spacecraft will support the station's operations and contribute to the ongoing studies conducted in microgravity. Upon completion of its mission, Cygnus XL will depart the ISS, carrying waste materials for disposal through atmospheric re-entry. This process is part of the routine maintenance and sustainability efforts of the space station, ensuring a clean and efficient environment for future missions.
Beyond the Headlines
The use of robotic technology like Canadarm2 in space operations underscores the importance of automation and precision in handling complex tasks in space. This technology not only enhances the efficiency of space missions but also reduces the risks associated with manual operations. The integration of such advanced systems is pivotal in paving the way for future missions, including those aimed at deeper space exploration and potential human settlement on other planets.