What's Happening?
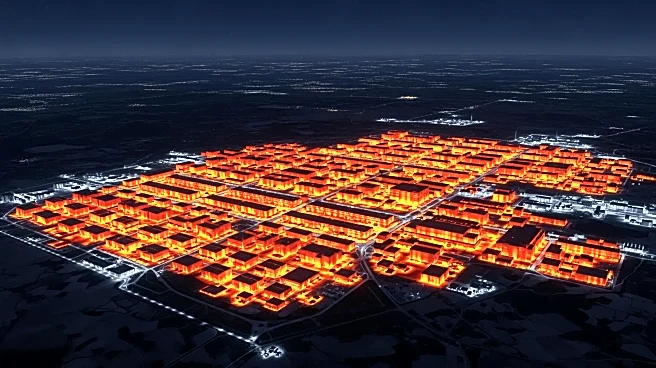
A new satellite image from the U.K.-based company SatVu has revealed the thermal footprint of one of the largest Bitcoin mining facilities in the U.S., located in Rockdale, Texas. The facility, known for its significant electricity consumption, uses about
700 megawatts of power, equivalent to the needs of 300,000 homes. The satellite image, captured by SatVu's heat-seeking technology, shows where and how much heat is leaking into the environment from the plant. This data provides insights into the environmental impact and operational activity of such facilities, which are often criticized for their high energy use and carbon footprint.
Why It's Important?
The revelation of heat emissions from the Bitcoin mining facility underscores the environmental challenges posed by cryptocurrency mining, which is known for its intensive energy consumption. As data centers and mining operations expand, they contribute significantly to electricity demand and carbon emissions. This development highlights the need for better regulatory oversight and innovative solutions to manage the environmental impact of such operations. The insights from SatVu's thermal data could aid regulators and grid operators in understanding and mitigating the effects of these facilities on local power networks and the environment.
Beyond the Headlines
The use of satellite technology to monitor heat emissions from industrial facilities represents a growing trend in leveraging space-based data for environmental monitoring. This approach provides an objective and real-time view of operational activities, offering a valuable tool for regulators and environmental advocates. As the cryptocurrency industry continues to grow, the pressure to adopt more sustainable practices and technologies will likely increase, potentially leading to innovations in energy efficiency and carbon reduction strategies.