What's Happening?
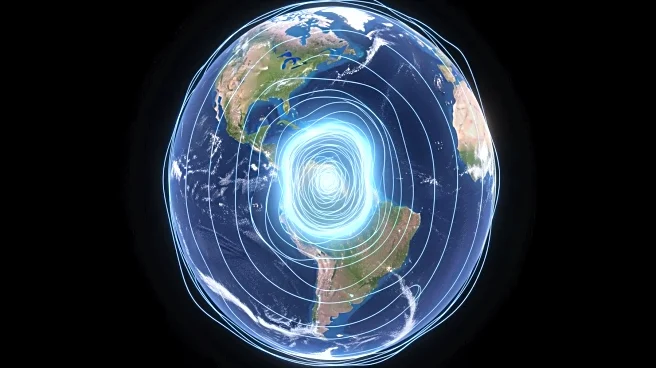
A significant weakening in Earth's magnetic field, known as the South Atlantic Anomaly, has been expanding rapidly over the past eleven years. This anomaly, located over the South Atlantic, has grown to cover an area equivalent to half the size of continental
Europe. The European Space Agency's Swarm satellites have been instrumental in tracking these changes, providing data that suggests the anomaly is behaving in unexpected ways. Researchers believe that a swirling body of molten iron in the Earth's outer core, approximately 1,800 miles below the surface, may be contributing to this phenomenon. However, other factors are also believed to be influencing the weakening of the magnetic field. The anomaly is not uniform, with different rates of change observed towards Africa and South America.
Why It's Important?
The expansion of the South Atlantic Anomaly has significant implications for navigation and space weather tracking, as the Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in these areas. The anomaly's growth could affect satellite operations and increase exposure to solar radiation in affected regions. Understanding the anomaly is vital for improving magnetic models that are essential for navigation systems. The research also highlights the complex interactions within the Earth's layers, which could provide insights into the planet's geophysical processes. The findings underscore the importance of continued monitoring and research to anticipate potential impacts on technology and infrastructure.
What's Next?
The European Space Agency plans to extend the Swarm mission beyond 2030, allowing for continued observation of the Earth's magnetic field. This extension will enable researchers to track the anomaly's behavior and further investigate the underlying causes of its expansion. The ongoing research aims to refine magnetic models and improve predictions related to space weather and navigation. As the anomaly continues to evolve, scientists will focus on understanding its implications for global technology systems and potential risks to satellite operations.
Beyond the Headlines
The South Atlantic Anomaly's expansion raises questions about the long-term stability of Earth's magnetic field and its potential effects on global systems. The anomaly's behavior could offer insights into the dynamics of the Earth's core and the processes driving magnetic field changes. This research may also contribute to broader discussions on planetary science and the factors influencing Earth's geophysical environment.