What is the story about?
What's Happening?
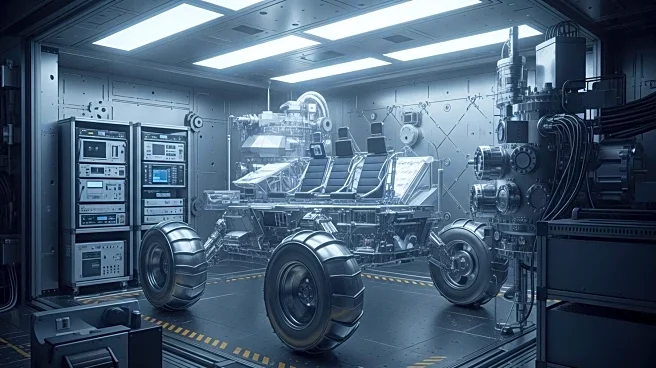
Starpath, a small business from Hawthorne, California, tested its lunar regolith excavation and transportation rover at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This opportunity was part of their prize for winning second place in NASA's Break the Ice Lunar Challenge. The challenge, which ran from 2020 to 2024, encouraged the development of robotic technologies capable of excavating and transporting lunar regolith. Starpath's rover, designed to operate in the harsh conditions of the lunar South Pole, was tested in a 20-foot thermal vacuum chamber. The chamber simulates the extreme environmental conditions found on the Moon. The rover features a dual drum barrel mechanism that mimics crab claws to efficiently excavate material without depleting its battery life.
Why It's Important?
The testing of Starpath's rover is significant as it contributes to NASA's efforts to develop technologies for future lunar missions, particularly those targeting the Moon's South Pole. This region is of interest due to the presence of ice within its regolith, which could be crucial for sustaining human presence on the Moon and for producing rocket fuel. The success of such technologies could enhance NASA's Artemis missions, which aim to return humans to the Moon and eventually send astronauts to Mars. The collaboration between NASA and private companies like Starpath highlights the importance of public-private partnerships in advancing space exploration technologies.
What's Next?
Starpath's rover testing is a step towards refining technologies needed for lunar exploration. As NASA continues to prepare for its Artemis missions, further development and testing of such technologies will be crucial. The data collected from these tests will inform future designs and improvements, potentially leading to more efficient and reliable systems for lunar and Martian exploration. Continued collaboration with private companies will likely play a key role in achieving these goals.