What's Happening?
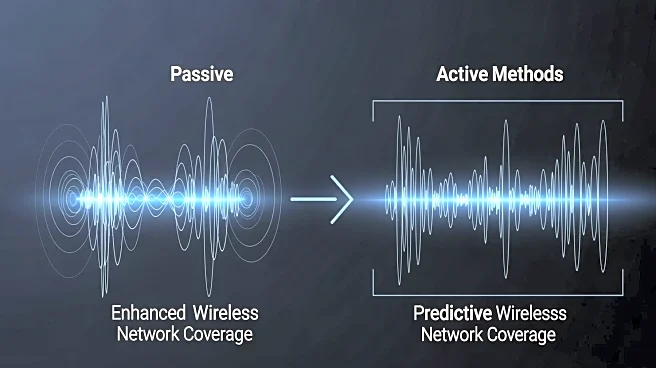
Wireless site surveys are essential for optimizing network coverage and performance, particularly in environments with dense Wi-Fi deployments like universities. There are three primary types of wireless
site surveys: passive, active, and predictive. Passive surveys involve listening to access points (APs) to gather data on signal strength and interference without directly connecting to the network. Active surveys, on the other hand, involve connecting to the network to measure performance metrics such as packet loss and latency. Predictive surveys use software to simulate AP coverage based on environmental factors like construction materials, providing a preliminary assessment of network design before physical surveys are conducted. These methods help network operators determine optimal AP placement and ensure robust coverage.
Why It's Important?
The effectiveness of wireless site surveys is crucial for institutions like universities, which rely heavily on stable and high-performance Wi-Fi networks to support educational activities and administrative functions. By accurately assessing network conditions and planning AP placements, these surveys help prevent coverage gaps and reduce interference, thereby enhancing the user experience. As educational institutions increasingly adopt digital tools and platforms, the demand for reliable wireless connectivity grows, making these surveys vital for maintaining operational efficiency. Moreover, the insights gained from these surveys can inform future upgrades and expansions, ensuring that networks can accommodate evolving technological needs.
What's Next?
Universities and other organizations are likely to continue leveraging predictive surveys as a cost-effective initial step in network planning, followed by onsite passive and active surveys to validate predictions. As technology advances, the integration of more sophisticated tools and software in conducting these surveys may improve accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, the adoption of new wireless standards, such as Wi-Fi 6E, may necessitate adjustments in survey methodologies to account for changes in frequency bands and network capabilities. Stakeholders in the education sector may also explore partnerships with technology providers to enhance survey processes and outcomes.
Beyond the Headlines
The growing complexity of wireless networks in educational settings highlights the need for ongoing research and development in survey technologies. Ethical considerations may arise regarding data privacy and security during active surveys, as these involve direct interaction with network infrastructure. Furthermore, the cultural shift towards digital learning environments underscores the importance of reliable connectivity as a fundamental component of modern education. Long-term, advancements in wireless site survey techniques could contribute to more sustainable and energy-efficient network designs, aligning with broader environmental goals.