What's Happening?
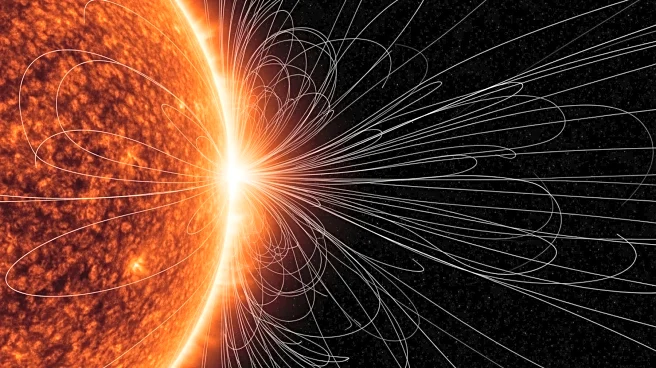
The European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter has captured the first close-up images of the sun's magnetic field near its south pole, revealing unexpected behaviors. The spacecraft's observations show bright arcs created by magnetic structures moving at high
speeds, indicating that the sun's magnetic field is migrating toward its poles faster than previously predicted. This discovery provides crucial insights into the sun's 11-year magnetic cycle, which influences solar phenomena such as sunspots and solar flares. The Solar Orbiter's unique orbit allows it to study the sun's polar regions, which have been largely unexplored until now.
Why It's Important?
Understanding the sun's magnetic field is vital for predicting solar activity that can impact Earth, such as solar storms that affect satellite communications and power grids. The new data from the Solar Orbiter offers valuable information about the sun's magnetic cycle, which is essential for improving models of solar behavior. This research could lead to better forecasting of solar events, helping to mitigate their effects on technology and infrastructure. Additionally, the findings contribute to the broader scientific understanding of the sun's influence on the solar system, enhancing our knowledge of space weather and its implications.
What's Next?
The Solar Orbiter's continued observations will provide more detailed data on the sun's magnetic field dynamics, potentially leading to new discoveries about solar processes. Researchers will analyze the data to refine models of the sun's magnetic cycle, improving predictions of solar activity. The mission may also inspire further studies and collaborations among scientists interested in solar physics and space weather. As the Solar Orbiter continues its mission, it will likely uncover more about the sun's polar regions, offering insights that could influence future space exploration and research.
Beyond the Headlines
The Solar Orbiter's findings highlight the importance of international collaboration in space research, as the mission involves contributions from multiple countries and organizations. The study of the sun's magnetic field also raises questions about the broader impact of solar activity on climate and environmental conditions on Earth. Understanding these connections could lead to advancements in climate science and environmental policy. Additionally, the mission underscores the significance of technological innovation in space exploration, as the Solar Orbiter's unique capabilities enable unprecedented observations of the sun.