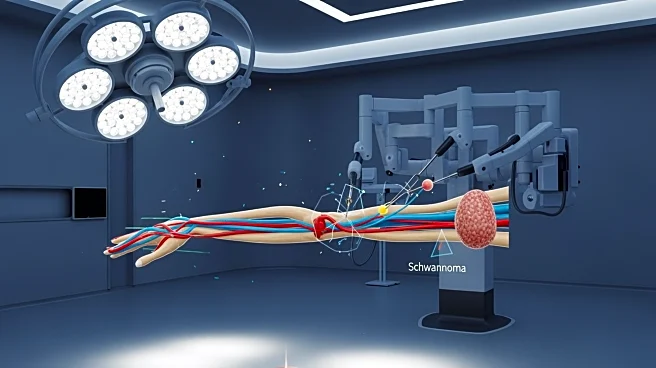
What's Happening?
A study has explored the clinical value of augmented reality (AR) navigation in the surgical treatment of brachial plexus schwannoma. Conducted at Jing’an District Central Hospital in Shanghai, the study involved
12 patients and utilized AR technology to improve surgical precision. The AR system, using a Microsoft HoloLens2, provided 3D visualization of the tumor and surrounding anatomy, aiding surgeons in planning and executing the procedure. The study found that AR navigation improved the accuracy of tumor localization and reduced intraoperative complications.
Why It's Important?
The use of AR in surgery represents a significant advancement in medical technology, offering enhanced visualization and precision. This can lead to better surgical outcomes, reduced recovery times, and fewer complications for patients. The technology's ability to provide real-time, detailed anatomical views could transform complex surgeries, making them safer and more efficient. As AR technology becomes more integrated into surgical practices, it could set new standards for patient care and surgical training.
What's Next?
Further research and clinical trials are expected to validate the efficacy of AR navigation in various surgical applications. As the technology matures, it may become a standard tool in operating rooms, particularly for complex procedures. The development of more sophisticated AR systems could also lead to broader adoption across different medical fields, enhancing the overall quality of healthcare.