What's Happening?
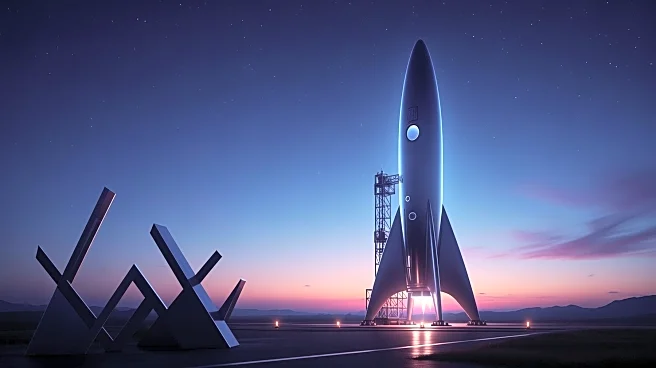
SpaceX's Starship, the largest rocket in the world, has launched in Texas, marking a significant step in the U.S. spaceflight program. The rocket is intended to transport NASA astronauts to the moon and eventually humans to Mars. However, SpaceX faces
challenges in maintaining its contract with NASA for the Artemis 3 mission, as concerns have been raised about delays in preparing Starship for the mission. Meanwhile, Chinese companies have been developing rockets that mimic SpaceX's designs, including a new spacecraft concept called Xingzhou-1 by Beijing Leading Rocket Technology. These developments highlight the competitive nature of the global space race.
Why It's Important?
The successful launch of SpaceX's Starship is crucial for the U.S. space program, particularly for NASA's Artemis mission, which aims to return humans to the moon. The competition from Chinese companies underscores the strategic importance of maintaining technological leadership in space exploration. If SpaceX fails to meet NASA's timelines, it could lose its lucrative contract, impacting its financial and strategic position. The imitation of SpaceX's designs by Chinese companies also raises concerns about intellectual property and the potential for increased competition in the space industry.
What's Next?
SpaceX is expected to launch the next prototype of Starship, known as Version 3, in 2026. This version aims to reach orbit and refuel its upper stage midflight, a capability necessary for missions to Mars. NASA's new administrator, Jared Isaacman, a close associate of Elon Musk, may influence the agency's decision on whether to continue with SpaceX for the Artemis 3 mission. The outcome of these developments will significantly impact the future of U.S. space exploration and SpaceX's role in it.