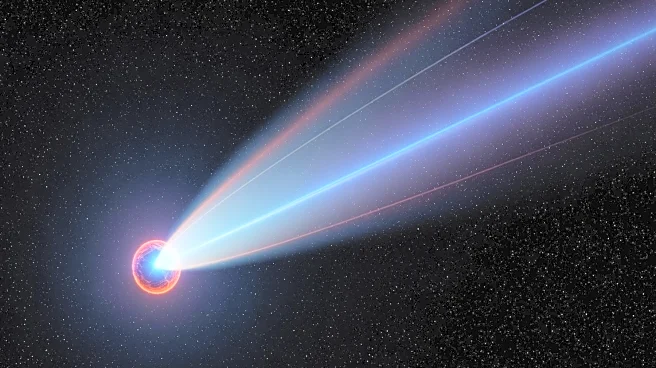
What's Happening?
The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is nearing its closest approach to the sun, known as perihelion, on October 29. This comet, believed to originate from a distant star system, is only the third interstellar object
ever detected in our solar system. It is noted for being the largest, fastest-moving, and potentially the oldest interstellar object observed. As it approaches the sun, the comet's ice is expected to vaporize, creating a visible tail. This event provides a unique opportunity for astronomers to study the comet using various instruments, potentially revealing new information about the outer regions of our galaxy.
Why It's Important?
The approach of 3I/ATLAS offers a rare chance to study an interstellar object in detail, which could enhance our understanding of the universe beyond our solar system. The data collected from this comet could provide insights into the composition and behavior of objects from other star systems, contributing to our knowledge of cosmic history and the formation of celestial bodies. This event is significant for the scientific community, as it may uncover secrets about the galaxy's outer reaches and the processes that govern interstellar travel.
What's Next?
As 3I/ATLAS reaches perihelion, it is expected to become more visible, allowing telescopes and other instruments to capture detailed observations. These observations will be crucial for scientists aiming to analyze the comet's composition and trajectory. The comet's departure from the solar system will be closely monitored, and the data collected will be studied to gain further insights into interstellar phenomena. This event may also inspire future missions to study similar objects, expanding our understanding of the universe.
Beyond the Headlines
The study of 3I/ATLAS could have long-term implications for our understanding of interstellar travel and the potential for life beyond Earth. By analyzing the materials and gases released by the comet, scientists may gain clues about the building blocks of life and the conditions necessary for its development. This research could influence future space exploration strategies and the search for extraterrestrial life.