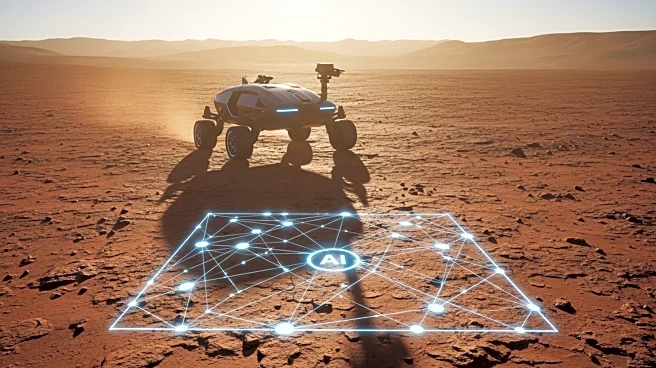
What's Happening?
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Anthropic have successfully conducted an experiment using artificial intelligence to determine the path of the Mars rover Perseverance. The AI, known as Claude
Code, analyzed Martian terrain data and satellite imagery to identify key terrain features and generate a path for the rover. This experiment aimed to improve efficiency and handle challenging terrain by specifying waypoints for the rover's journey. The AI-directed runs were conducted on December 8 and December 10, 2025, covering a total distance of 456 meters. The project team tested over 500,000 variables using Perseverance's digital twin to ensure the AI's instructions were suitable. Human engineers further refined these instructions using additional surface camera imagery.
Why It's Important?
The successful use of AI in navigating the Mars rover Perseverance represents a significant advancement in space exploration technology. By automating the route planning process, NASA can potentially reduce the time spent on planning by half, allowing more focus on exploration and data collection. This development could lead to more efficient and effective missions, enhancing our understanding of Mars and potentially other celestial bodies. The collaboration between NASA and Anthropic highlights the growing role of AI in scientific research and exploration, potentially setting a precedent for future missions.
What's Next?
As AI route planning becomes fully implemented, NASA and Anthropic anticipate spending more time on exploration and data collection. The success of this experiment may lead to further integration of AI in space missions, potentially expanding its use to other rovers and missions. The continued refinement and testing of AI systems will be crucial to ensure their reliability and effectiveness in the challenging environments of space exploration.